Urinary endotrophin predicts disease progression in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 29229941
- PMCID: PMC5725589
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17470-3
Urinary endotrophin predicts disease progression in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
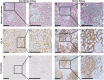
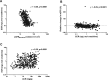
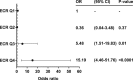
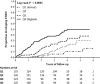
Renal fibrosis is the central pathogenic process in progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Collagen type VI (COL VI) is upregulated in renal fibrosis. Endotrophin is released from COL VI and promotes pleiotropic pro-fibrotic effects. Kidney disease severity varies considerably and accurate information regarding CKD progression may improve clinical decisions. We tested the hypothesis that urinary endotrophin derived during COL VI deposition in fibrotic human kidneys is a marker for progression of CKD in the Renal Impairment in Secondary Care (RIISC) cohort, a prospective observational study of 499 CKD patients. Endotrophin localised to areas of increased COL VI deposition in fibrotic kidneys but was not present in histologically normal kidneys. The third and fourth quartiles of urinary endotrophin:creatinine ratio (ECR) were independently associated with one-year disease progression after adjustment for traditional risk factors (OR (95%CI) 3.68 (1.06-12.83) and 8.65 (2.46-30.49), respectively). Addition of ECR quartiles to the model for disease progression increased prediction as seen by an increase in category-free net reclassification improvement (0.45, 95% CI 0.16-0.74, p = 0.002) and integrated discrimination improvement (0.04, 95% CI 0.02-0.06, p < 0.001). ECR was associated with development of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). It is concluded that ECR predicts disease progression of CKD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
D.G.K.R., M.A.K. and F.G. are full-time employees at Nordic Bioscience. Nordic Bioscience is a privately-owned, small–medium size enterprise partly focused on the development of biomarkers. None of the authors received fees, bonuses or other benefits for the work described in the manuscript. M.A.K. holds stocks in Nordic Bioscience. The patent for the ELISA used to assess endotrophin levels (the PRO-C6 ELISA) is owned by Nordic Bioscience. The funder provided support in the form of salaries for authors D.G.K.R., M.A.K. and F.G., but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. All other authors report no competing financial interests relevant to this manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

