Prevalence, treatment patterns, and risk factors of hypertension and pre-hypertension among Bangladeshi adults
- PMID: 29230005
- PMCID: PMC5860750
- DOI: 10.1038/s41371-017-0018-x
Prevalence, treatment patterns, and risk factors of hypertension and pre-hypertension among Bangladeshi adults
Abstract
In Bangladesh, morbidity and mortality due to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) has increased over the last few decades. Hypertension is an important risk factor for NCDs, specifically cardiovascular disease. The objective of this study was to assess prevalence and risk factors for hypertension and pre-hypertension among adults in Bangladesh. Data for this analysis were collected during the national NCD Risk Factor Survey of Bangladesh conducted in 2010 from a representative sample of men and women, aged 25 years or above. The survey adopted a multistage, geographically clustered, probability-based sampling approach. WHO STEPS questionnaire was used to collect data on demographics, behavioral risk factors, and physical measurements. Overall, 20% of the study population were hypertensive at study measurement. The prevalence of hypertension increased with age and body mass index (BMI). Twelve percent of the population were previously diagnosed with hypertension. Among these individuals, nearly half were not taking any medications to control their hypertension. Additionally, the prevalence of pre-hypertension was 43%, with higher levels among males, older age groups, and those with higher education, higher wealth index and high BMI. Predictors of hypertension, included older age, high BMI, and diabetes comorbidity. Based on this study, we estimate that 1 out of 5 Bangladeshi adults have hypertension. The risk of hypertension increases with older age and high BMI. Additionally, prevalence of pre-hypertension is high in Bangladesh in both rural and urban areas. Findings from this study can be used to inform public health programming to control the spread of NCDs in Bangladesh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this study declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
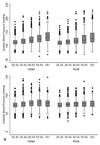
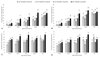

References
-
- A global brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, global public health crisis. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (London, England) 2012;380(9859):2224–60. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

