Nanoparticle orientation to control RNA loading and ligand display on extracellular vesicles for cancer regression
- PMID: 29230043
- PMCID: PMC5762263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-017-0012-z
Nanoparticle orientation to control RNA loading and ligand display on extracellular vesicles for cancer regression
Abstract
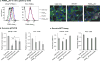
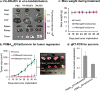
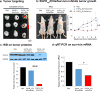
Nanotechnology offers many benefits, and here we report an advantage of applying RNA nanotechnology for directional control. The orientation of arrow-shaped RNA was altered to control ligand display on extracellular vesicle membranes for specific cell targeting, or to regulate intracellular trafficking of small interfering RNA (siRNA) or microRNA (miRNA). Placing membrane-anchoring cholesterol at the tail of the arrow results in display of RNA aptamer or folate on the outer surface of the extracellular vesicle. In contrast, placing the cholesterol at the arrowhead results in partial loading of RNA nanoparticles into the extracellular vesicles. Taking advantage of the RNA ligand for specific targeting and extracellular vesicles for efficient membrane fusion, the resulting ligand-displaying extracellular vesicles were capable of specific delivery of siRNA to cells, and efficiently blocked tumour growth in three cancer models. Extracellular vesicles displaying an aptamer that binds to prostate-specific membrane antigen, and loaded with survivin siRNA, inhibited prostate cancer xenograft. The same extracellular vesicle instead displaying epidermal growth-factor receptor aptamer inhibited orthotopic breast cancer models. Likewise, survivin siRNA-loaded and folate-displaying extracellular vesicles inhibited patient-derived colorectal cancer xenograft.
Conflict of interest statement
P. Guo’s Sylvan G. Frank Endowed Chair position in Pharmaceutics and Drug Delivery is funded by the CM Chen Foundation, and he is a consultant of Oxford Nanopore, Nanobio Delivery Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, and the cofounder of P&Z Biological Technology LLC. Pi now works for Nanobio Delivery Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, S. Wang and F. Haque now work for P&Z Biological Technology LLC.
Figures



References
-
- Guo P, Erickson S, Anderson D. A small viral RNA is required for in vitro packaging of bacteriophage phi29 DNA. Science. 1987;236:690–694. - PubMed
-
- Guo P, Zhang C, Chen C, Trottier M, Garver K. Inter-RNA interaction of phage phi29 pRNA to form a hexameric complex for viral DNA transportation. Mol Cell. 1998;2:149–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

