Non-Canonical Mechanisms Regulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha in Cancer
- PMID: 29230384
- PMCID: PMC5711814
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00286
Non-Canonical Mechanisms Regulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha in Cancer
Abstract
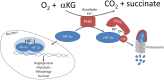
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) orchestrates cellular adaptation to low oxygen and nutrient-deprived environment and drives progression to malignancy in human solid cancers. Its canonical regulation involves prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs), which in normoxia induce degradation, whereas in hypoxia allow stabilization of HIF-1α. However, in certain circumstances, HIF-1α regulation goes beyond the actual external oxygen levels and involves PHD-independent mechanisms. Here, we gather and discuss the evidence on the non-canonical HIF-1α regulation, focusing in particular on the consequences of mitochondrial respiratory complexes damage on stabilization of this pleiotropic transcription factor.
Keywords: cancer; electron transport chain; hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; mitochondria; oxidative phosphorylation; prolyl hydroxylases; pseudohypoxia; pseudonormoxia.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

