Placenta microstructure and microcirculation imaging with diffusion MRI
- PMID: 29230859
- PMCID: PMC5947291
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27036
Placenta microstructure and microcirculation imaging with diffusion MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To assess which microstructural models best explain the diffusion-weighted MRI signal in the human placenta.
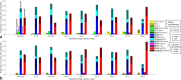
Methods: The placentas of nine healthy pregnant subjects were scanned with a multishell, multidirectional diffusion protocol at 3T. A range of multicompartment biophysical models were fit to the data, and ranked using the Bayesian information criterion.
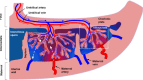
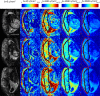
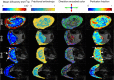
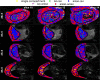
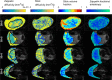
Results: Anisotropic extensions to the intravoxel incoherent motion model, which consider the effect of coherent orientation in both microvascular structure and tissue microstructure, consistently had the lowest Bayesian information criterion values. Model parameter maps and model selection results were consistent with the physiology of the placenta and surrounding tissue.
Conclusion: Anisotropic intravoxel incoherent motion models explain the placental diffusion signal better than apparent diffusion coefficient, intravoxel incoherent motion, and diffusion tensor models, in information theoretic terms, when using this protocol. Future work will aim to determine if model-derived parameters are sensitive to placental pathologies associated with disorders, such as fetal growth restriction and early-onset pre-eclampsia. Magn Reson Med 80:756-766, 2018. © 2017 The Authors Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Keywords: Bayesian information criterion; diffusion MRI; intravoxel incoherent motion; microstructure; model selection; placenta.
© 2017 The Authors Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Nelson DM. How the placenta affects your life, from womb to tomb. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015;213:S12–S13. - PubMed
-
- Vedmedovska N, Rezeberga D, Teibe U, Melderis I, Donders GGG. Placental pathology in fetal growth restriction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2011;155:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Mifsud W, Sebire NJ. Placental pathology in early‐onset and late‐onset fetal growth restriction. Fetal Diagn Therapy 2014;36:117–128. - PubMed
-
- Veerbeek JHW, Nikkels PGJ, Torrance HL, Gravesteijn J, Post Uiterweer ED, Derks JB, Koenen SV, Visser GHA, Van Rijn BB, Franx A. Placental pathology in early intrauterine growth restriction associated with maternal hypertension. Placenta 2014;35:696–701. - PubMed
-
- Myatt L. Role of placenta in preeclampsia. Endocrine 2002;19:103–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

