China's Silk Road and global health
- PMID: 29231838
- PMCID: PMC7159269
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32898-2
China's Silk Road and global health
Abstract
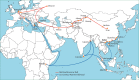
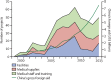
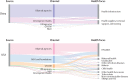
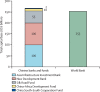
In 2013, China proposed its Belt and Road Initiative to promote trade, infrastructure, and commercial associations with 65 countries in Asia, Africa, and Europe. This initiative contains important health components. Simultaneously, China launched an unprecedented overseas intervention against Ebola virus in west Africa, dispatching 1200 workers, including Chinese military personnel. The overseas development assistance provided by China has been increasing by 25% annually, reaching US$7 billion in 2013. Development assistance for health from China has particularly been used to develop infrastructure and provide medical supplies to Africa and Asia. China's contributions to multilateral organisations are increasing but are unlikely to bridge substantial gaps, if any, vacated by other donors; China is creating its own multilateral funds and banks and challenging the existing global architecture. These new investment vehicles are more aligned with the geography and type of support of the Belt and Road Initiative. Our analysis concludes that China's Belt and Road Initiative, Ebola response, development assistance for health, and new investment funds are complementary and reinforcing, with China shaping a unique global engagement impacting powerfully on the contours of global health.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hu R, Liu R, Hu N. China's Belt and Road Initiative from a global health perspective. Lancet Glob Heal. 2017;5:e752–e753. - PubMed
-
- Wu G, for National Health and Family Planning Commission Building the Silk Road with health. http://en.nhfpc.gov.cn/2017-01/20/c_71075.htm (accessed July 18, 2017).
-
- Jaspal ZN, for Pakistan Observer CPEC & OBOR: portents of progress. http://pakobserver.net/cpec-obor-portents-progress/ (accessed July 18, 2017).
-
- National Health and Family Planning Commission Beijing Communique, Silk Road-Belt High Level Health Conference. Aug 18, 2017. http://en.nhfpc.gov.cn/2017-08/18/c_72257.htm (accessed Aug 30, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

