Behavior-driven arc expression is reduced in all ventral hippocampal subfields compared to CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus in rat dorsal hippocampus
- PMID: 29232477
- PMCID: PMC5777901
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.22820
Behavior-driven arc expression is reduced in all ventral hippocampal subfields compared to CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus in rat dorsal hippocampus
Abstract
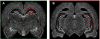
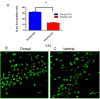
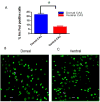
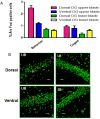
Anatomical connectivity and lesion studies reveal distinct functional heterogeneity along the dorsal-ventral axis of the hippocampus. The immediate early gene Arc is known to be involved in neural plasticity and memory and can be used as a marker for cell activity that occurs, for example, when hippocampal place cells fire. We report here, that Arc is expressed in a greater proportion of cells in dorsal CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG), following spatial behavioral experiences compared to ventral hippocampal subregions (dorsal CA1 = 33%; ventral CA1 = 13%; dorsal CA3 = 23%; ventral CA3 = 8%; and dorsal DG = 2.5%; ventral DG = 1.2%). The technique used here to obtain estimates of numbers of behavior-driven cells across the dorsal-ventral axis, however, corresponds quite well with samples from available single unit recording studies. Several explanations for the two- to-threefold reduction in spatial behavior-driven cell activity in the ventral hippocampus can be offered. These include anatomical connectivity differences, differential gain of the self-motion signals that appear to alter the scale of place fields and the proportion of active cells, and possibly variations in the neuronal responses to non-spatial information within the hippocampus along its dorso-ventral axis.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Alme CB, Buzzetti RA, Marrone DF, Leutgeb JK, Chawla MK, Schaner MJ, Bohanick JD, Khoboko T, Leutgeb S, Moser EI, et al. Hippocampal granule cells opt for early retirement. Hippocampus. 2010;20:1109–1123. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP. The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience. 1989;31:571–591. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JNP, McHugh SB, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang W-N, Pothuizen HHJ, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus--memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Yee BK, Good MA, Heupel MJ, Iversen SD, Rawlins JN. Double dissociation of function within the hippocampus: a comparison of dorsal, ventral, and complete hippocampal cytotoxic lesions. Behav. Neurosci. 1999;113:1170–1188. - PubMed
-
- Beer Z, Chwiesko C, Sauvage MM. Processing of spatial and non-spatial information reveals functional homogeneity along the dorso-ventral axis of CA3, but not CA1. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014;111:56–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

