Salidroside attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance by upregulating autophagy through the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway
- PMID: 29233105
- PMCID: PMC5726034
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-017-0477-4
Salidroside attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance by upregulating autophagy through the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have shown that both adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) are energy sensors and are related to autophagy. Our recent reports have shown that salidroside can exert protective effects against hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation and apoptosis resistance through the AMPK pathway. This study aims to explore the relationship among AMPK, mTOR and ULK1 in PASMCs under hypoxic conditions and to investigate whether the protective effects of salidroside are related to the autophagic cell death pathway.
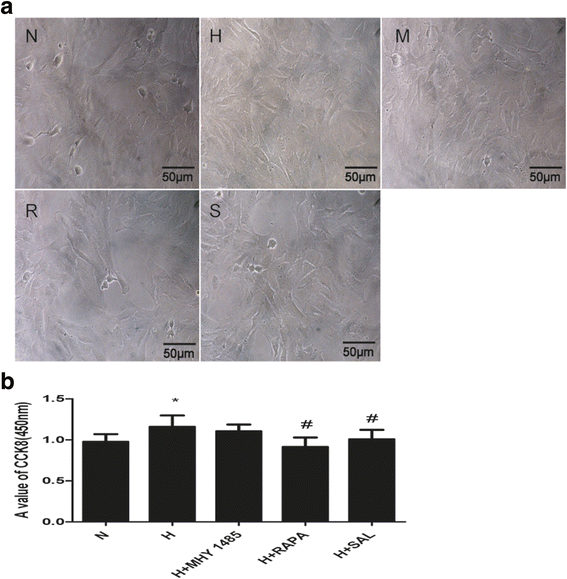
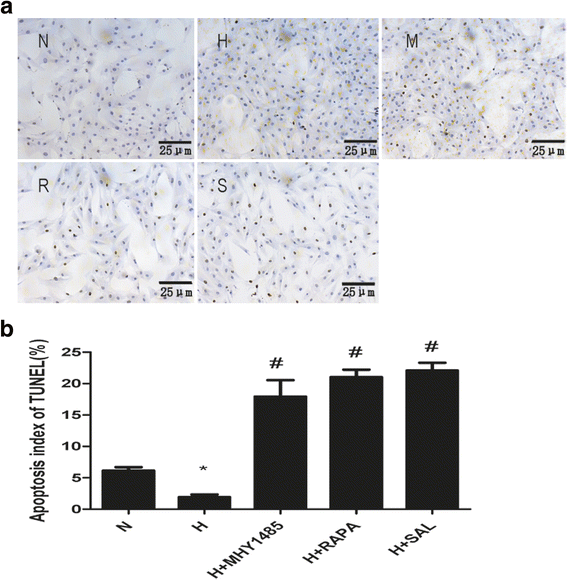
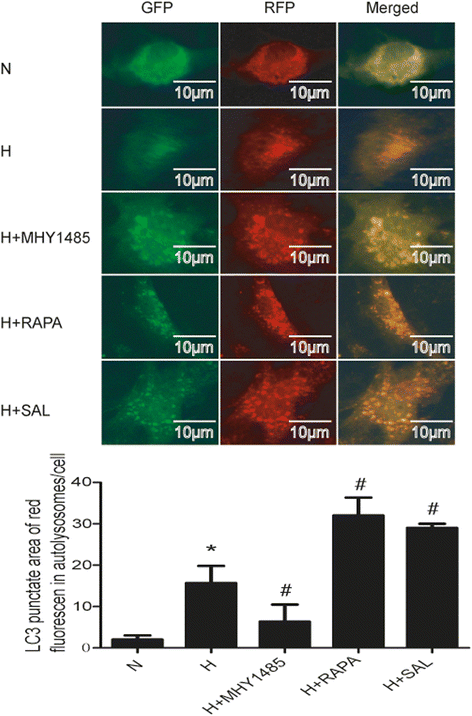
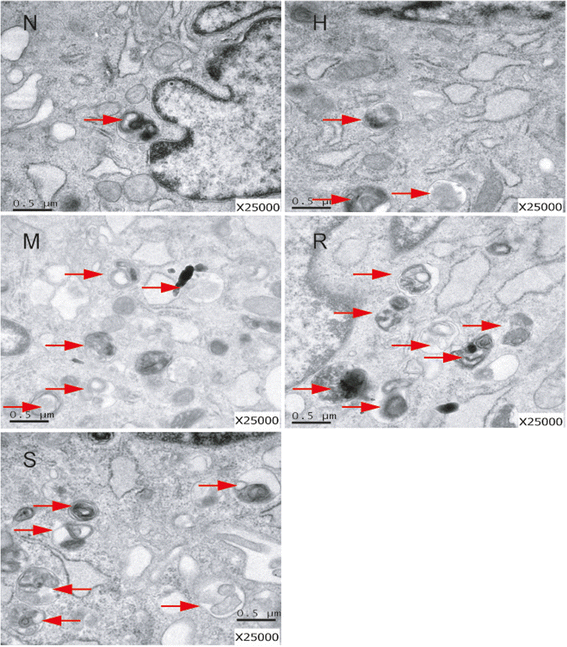
Methods: Rat PASMCs were cultured and divided into five groups: the normoxia, hypoxia, hypoxia + MHY1485 (mTOR agonist), hypoxia + rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor) and hypoxia + salidroside groups. Hypoxic cells were treated as indicated for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated by the CCK-8 assay. Cell apoptosis was measured by the TUNEL assay. The autophagy flux of PASMCs was evaluated with tandem mRFP-GFP fluorescence microscopy. Autophagosomes were detected by electron microscopy. Protein expression of LC3, p62, AMPK, P-AMPK (Thr 172), P-ULK1 (Ser 555 and Ser 317), mTOR, P-mTOR (Ser 2448), ULK1 and P-ULK1 (Ser 757) was detected by western blot assay.
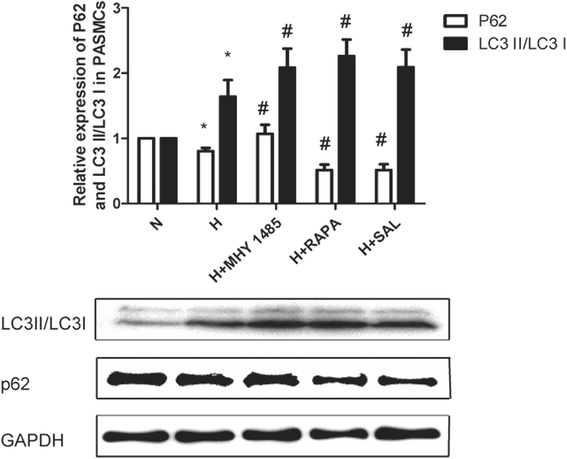
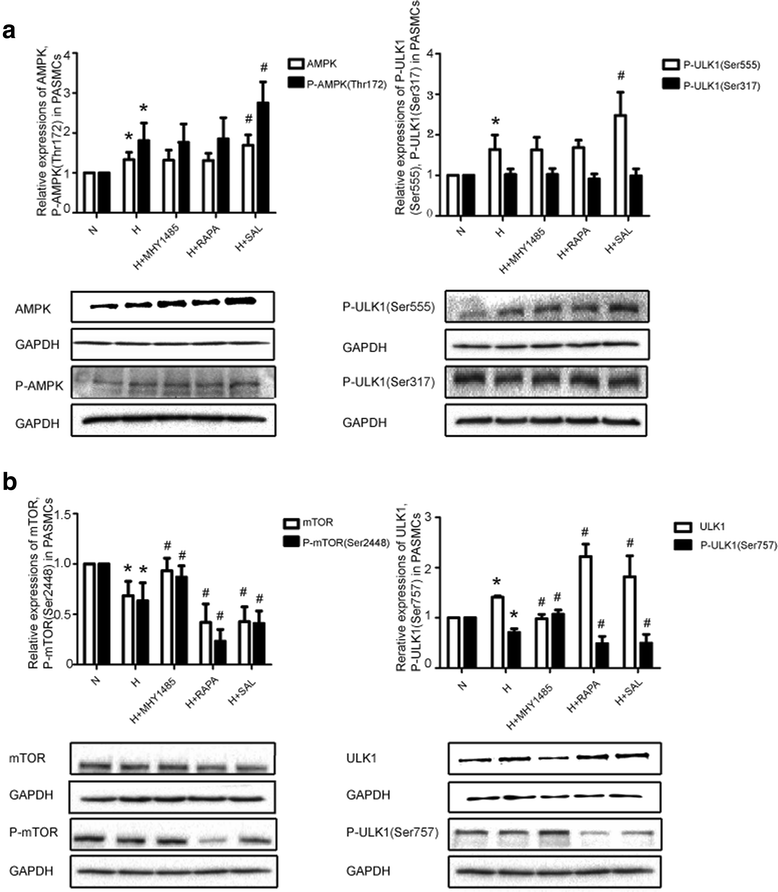
Results: PASMC proliferation and apoptosis resistance were observed under hypoxic conditions. Autophagy flux, the number of autophagosomes and the LC3II/LC3I ratio were increased in the hypoxia group compared with the normoxia group, whereas p62 expression was decreased. Treatment with rapamycin or salidroside reversed hypoxia-induced PASMC proliferation and apoptosis resistance and further increased autophagy flux, autophagosome levels and the LC3II/LC3I ratio but decreased p62 expression. Treatment with MHY1485 reversed hypoxia-induced PASMC apoptosis resistance and decreased autophagy flux as well as increased autophagosome levels, the LC3II/LC3I ratio and p62 expression. P-AMPK (Thr 172) and P-ULK1 (Ser 555) of the AMPK-ULK1 pathway were increased in the hypoxia group and were further increased in the salidroside group. Rapamycin and MHY1485 had no effect on either P-AMPK (Thr 172) or P-ULK1 (Ser 555). Phosphorylation of ULK1 at serine 317 did not significantly affect the five groups. Furthermore, P-mTOR (Ser 2448) and P-ULK1 (Ser 757) of the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway were decreased in the hypoxia group and were further decreased in the salidroside group. MHY1485 increased the expression of both P-mTOR(Ser 2448) and P-ULK1(Ser 757), whereas rapamycin had the opposite effect.
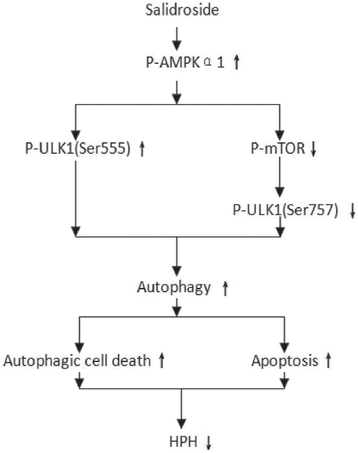
Conclusions: Salidroside might inhibit hypoxia-induced PASMC proliferation and reverse apoptosis resistance via the upregulation of autophagy through both the AMPKα1-ULK1 and AMPKα1-mTOR-ULK1 pathways.
Keywords: Ampk; Autophagy; Hypoxia; PASMCs; ULK1; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All experimental protocols were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institute of Health and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Wenzhou Medical University. Additionally, all animals were handled humanely during the study protocol and during euthanasia.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Protective Effects of Κ-Opioid Receptor Stimulation in Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension Involve Inhibition of Autophagy Through the AMPK-MTOR Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1965-1979. doi: 10.1159/000485886. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29224002
-
Tris (1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate induces apoptosis and autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells: Involvement of ROS-mediated AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathways.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Feb;100:183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.12.029. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28025121
-
Melatonin attenuates vascular calcification by activating autophagy via an AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Apr 1;389(1):111883. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111883. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32014443
-
Hernandezine Regulates Proliferation and Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Melanoma Cells.J Nat Prod. 2022 May 27;85(5):1351-1362. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00098. Epub 2022 May 11. J Nat Prod. 2022. PMID: 35544345 Review.
-
The mechanism of UNC-51-like kinase 1 and the applications of small molecule modulators in cancer treatment.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Mar 15;268:116273. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116273. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38432059 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D3 promotes gastric cancer cell autophagy by mediating p53/AMPK/mTOR signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1338260. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1338260. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38259281 Free PMC article.
-
Alogliptin improves survival and health of mice on a high-fat diet.Aging Cell. 2019 Apr;18(2):e12883. doi: 10.1111/acel.12883. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Aging Cell. 2019. PMID: 30644630 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside suppresses cell growth and inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase/threonine kinase signaling in rheumatoid arthritis.Z Rheumatol. 2024 Feb;83(Suppl 1):78-87. doi: 10.1007/s00393-023-01431-5. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Z Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 37851166 English.
-
Analysis of lncRNAs Expression Profiles in Hair Follicle of Hu Sheep Lambskin.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jun 15;10(6):1035. doi: 10.3390/ani10061035. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32549352 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin 1 receptor attenuates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage by controlling mitochondrial metabolism via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway in rats.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):522-539. doi: 10.7150/thno.49426. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391490 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

