Association between risk of asthma and gene polymorphisms in CHI3L1 and CHIA: a systematic meta-analysis
- PMID: 29233108
- PMCID: PMC5726029
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-017-0515-2
Association between risk of asthma and gene polymorphisms in CHI3L1 and CHIA: a systematic meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have indicated that chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) gene rs4950928 polymorphism and acidic mammalian chitinase (AMCase or CHIA) gene rs10494132 polymorphism are associated with the risk of asthma. However, the results are inconsistent because of small sample size and varied ethnicity and age in studies. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis was important to clarify the effect of CHI3L1 rs4950928 polymorphism and CHIA rs10494132 variant on asthma risk.
Methods: An electronic literature search was conducted to identify all the eligible studies. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated and sensitivity analysis as well as publication bias were assessed to investigate the associations. All statistical analyses were performed using STATA 12.0.
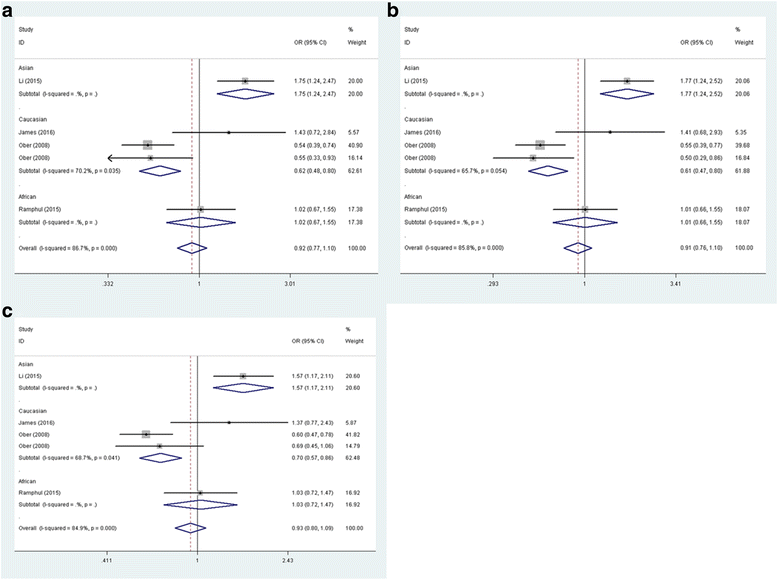
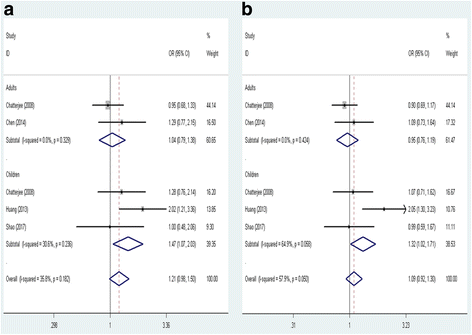
Results: Eight published articles with 10 case-control studies were included, 5 studies were of CHI3L1 rs4950928 polymorphism and another 5 studies involved CHIA rs10494132 polymorphism. Overall, no significant association was found between CHI3L1 polymorphism and asthma susceptibility. After stratified according to ethnicity, CHI3L1 rs4950928 variant was associated with decreased asthma risk in Caucasians (GG + GC vs. CC: OR = 0.621, 95% CI = 0.484-0.797, P = 0.000; GC vs. CC: OR = 0.612, 95% CI = 0.470-0.796, P = 0.000; G vs. C: OR = 0.696, 95% CI = 0.567-0.856, P = 0.001). When stratified population by age, there was no association in children under all genetic models. As for CHIA rs10494132 polymorphism, no evidence of association between CHIA rs10494132 polymorphism and asthma risk was identified. Furthermore, subgroup analysis by ethnicity revealed a positive correlation between CHIA rs10494132 polymorphism and asthma risk among Asians (TT vs. TC + CC: OR = 1.476, 95% CI = 1.071-2.032, P = 0.017; T vs. C: OR = 1.326, 95% CI = 1.024-1.717, P = 0.032). Additionally, in the subgroup analysis conducted according to age, CHIA rs10494132 variant was also found to be associated with the increased risk of asthma in children (TT vs. TC + CC: OR = 1.472, 95% CI = 1.067-2.030, P = 0.019; T vs. C: OR = 1.320, 95% CI = 1.016-1.713, P = 0.037).
Conclusions: The G allele of CHI3L1 rs4950928 might be a protective factor against the development of asthma. However, the rs10494132 polymorphism of CHIA might be a risk factor for asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; CHI3L1; CHIA; Gene polymorphism; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Authors declare no financial affiliations or conflicts of interest in submitting the study for publication.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional study of the association of CHI3L1 polymorphisms with asthma susceptibility in the Southwest Chinese Han population.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 14;39(5):BSR20182008. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182008. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30988078 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Association between Genetic Polymorphisms in the CHI3L1 Gene and Asthma Risk.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022;183(8):907-918. doi: 10.1159/000522393. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35340006
-
Chitinase 3-like 1 polymorphisms and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma in a Chinese population.J Gene Med. 2020 Sep;22(9):e3208. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3208. Epub 2020 May 29. J Gene Med. 2020. PMID: 32367614
-
The chitinase and chitinase-like proteins: a review of genetic and functional studies in asthma and immune-mediated diseases.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Oct;9(5):401-8. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283306533. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19644363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Gene Polymorphisms of T Cell Immunoglobulin Domain and Mucin Domain-3 and Risk of Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021 Feb 11;20(1):1-10. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v20i1.5407. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33639624
Cited by
-
Functional study of the association of CHI3L1 polymorphisms with asthma susceptibility in the Southwest Chinese Han population.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 14;39(5):BSR20182008. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182008. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30988078 Free PMC article.
-
The mammalian acid chitinase promotes oncogenic properties of thyroid cancer cells through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Eur Thyroid J. 2025 Apr 25;14(2):e240311. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-24-0311. Print 2025 Apr 1. Eur Thyroid J. 2025. PMID: 40198658 Free PMC article.
-
Responsiveness of Inhaled Corticosteroid Treatment in Children with Asthma: The Role of rs242941 Polymorphism of CRHR1 Gene.Pulm Ther. 2023 Mar;9(1):127-137. doi: 10.1007/s41030-022-00205-9. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Pulm Ther. 2023. PMID: 36459327 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin-2 Receptor Agonists Produce Anti-inflammatory Effects through Functionally Selective Mechanisms That Involve the Suppression of Disease-Induced Arginase 1 Expression.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jan 25;7(2):478-492. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00297. eCollection 2024 Feb 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38357283 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic studies on the role of CHI3L1 in eosinophilic inflammation in chronic sinusitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 25;16:1562546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1562546. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40201175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mims JW. Asthma: definitions and pathophysiology. International forum of allergy & rhinology. 2015; 5 Suppl 1: S2-S6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

