Low prevalence of lipid metabolism abnormalities in APOE ε2-genotype and male patients 60 years or older with schizophrenia
- PMID: 29233125
- PMCID: PMC5727937
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-017-1530-9
Low prevalence of lipid metabolism abnormalities in APOE ε2-genotype and male patients 60 years or older with schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder largely manageable with atypical antipsychotics; however, these drugs have been associated with glucose/lipid metabolism issues such as diabetes and hyperlipidaemia. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is the most abundant apolipoprotein, and APOE genotypes have been correlated with lipid metabolism phenotypes in an age-dependent manner. Studies examining the relationship between the APOE genotype and lipid abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia have been inconclusive, but primarily focused on adult patient populations. Therefore, we explored the correlations between the APOE genotype and glucose/lipid metabolism indicators and abnormalities in hospitalized patients 60 years or older with schizophrenia with a history of long-term antipsychotics use.
Methods: We assessed APOE genotype, age, weight, height, blood glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein in a total of 294 patients. APOE genotypes were divided into three groups: APOE ε2 (ε2/ε2 and ε2/ε3), APOE ε3 (ε3/ε3), and APOE ε4 (ε3/ε4 and ε4/ε4), and comparisons were conducted among these groups or according to ε2 carrier status.
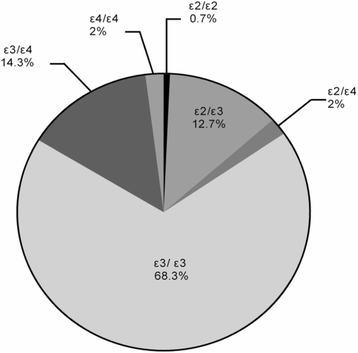
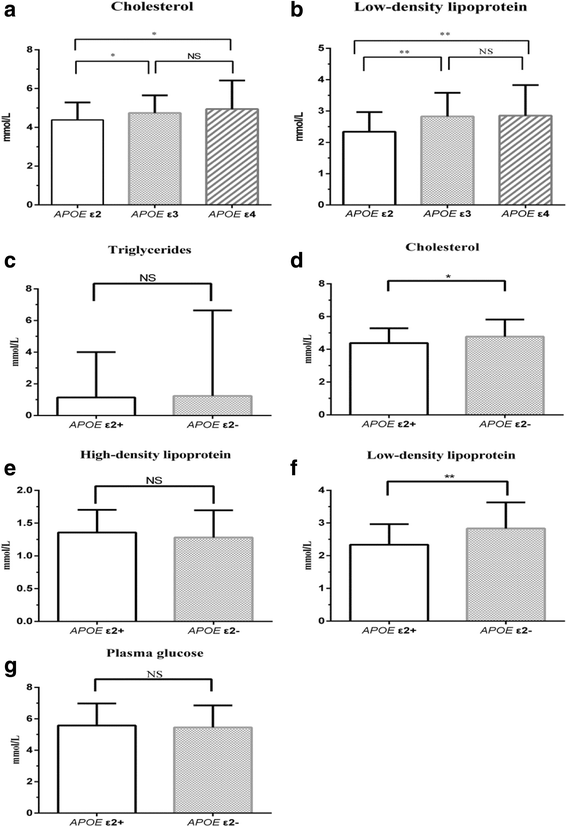
Results: APOE ε3/ε3 was the most common genotype (68.3%) and at least one ε3 allele was present in 81.8% of patients. There were no differences in antipsychotics type or dose according to the APOE genotype, but serum cholesterol values varied near significantly (P = 0.052) and low-density lipoprotein values varied significantly according to genotype (P < 0.05, lowest in the APOE ε2 genotype). Men had lower cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels (P < 0.05) than women. Compared to patients administered typical antipsychotics, those administered atypical antipsychotics had higher triglyceride, cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels (P < 0.05). Stepwise linear regressions showed that cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels were influenced by sex, the APOE ε2 genotype, and atypical antipsychotics use.
Conclusions: In the context of atypical antipsychotics use, carriers of the APOE ε2-genotype and male patients with schizophrenia 60 years or older may be less likely to develop a lipid metabolism abnormality.
Background: Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder largely manageable with atypical antipsychotics; however, these drugs have been associated with glucose/lipid metabolism issues such as diabetes and hyperlipidaemia. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is the most abundant apolipoprotein, and APOE genotypes have been correlated with lipid metabolism phenotypes in an age-dependent manner. Studies examining the relationship between the APOE genotype and lipid abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia have been inconclusive, but primarily focused on adult patient populations. Therefore, we explored the correlations between the APOE genotype and glucose/lipid metabolism indicators and abnormalities in hospitalized patients 60 years or older with schizophrenia with a history of long-term antipsychotics use.
Methods: We assessed APOE genotype, age, weight, height, blood glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein in a total of 294 patients. APOE genotypes were divided into three groups: APOE ε2 (ε2/ε2 and ε2/ε3), APOE ε3 (ε3/ε3), and APOE ε4 (ε3/ε4 and ε4/ε4), and comparisons were conducted among these groups or according to ε2 carrier status.
Results: APOE ε3/ε3 was the most common genotype (68.3%) and at least one ε3 allele was present in 81.8% of patients. There were no differences in antipsychotics type or dose according to the APOE genotype, but serum cholesterol values varied near significantly (P = 0.052) and low-density lipoprotein values varied significantly according to genotype (P < 0.05, lowest in the APOE ε2 genotype). Men had lower cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels (P < 0.05) than women. Compared to patients administered typical antipsychotics, those administered atypical antipsychotics had higher triglyceride, cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels (P < 0.05). Stepwise linear regressions showed that cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels were influenced by sex, the APOE ε2 genotype, and atypical antipsychotics use.
Conclusions: In the context of atypical antipsychotics use, carriers of the APOE ε2-genotype and male patients with schizophrenia 60 years or older may be less likely to develop a lipid metabolism abnormality.
Keywords: APOE; Cholesterol; Elderly schizophrenia; Glucose; HDL; LDL; Triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shanghai Mental Health Center. Written informed consent was provided by all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of apolipoprotein-E polymorphism and plasma lipid levels in dyslipidemic and asymptomatic subjects, and their implication in cardio/cerebro-vascular disorders.Neurochem Int. 2010 Jan;56(1):177-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.09.016. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Neurochem Int. 2010. PMID: 19819279
-
Enhanced Diabetes Susceptibility in Community Dwelling Han Elders Carrying the Apolipoprotein E 3/3 Genotype.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 21;11(3):e0151336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151336. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26998902 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) Mass Levels Increase Significantly According to APOE Genotype: An Analysis of 431 239 Patients.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Mar;37(3):580-588. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308704. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28062489 Free PMC article.
-
Association of apolipoprotein E genotypes with lipid levels and coronary risk.JAMA. 2007 Sep 19;298(11):1300-11. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.11.1300. JAMA. 2007. PMID: 17878422 Review.
-
APOE2: protective mechanism and therapeutic implications for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2020 Nov 4;15(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00413-4. Mol Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 33148290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Homozygosity in the APOE 3 Polymorphism Is Associated With Less Depression and Higher Serum Low-Density Lipoprotein in Chinese Elderly Schizophrenics.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 15;11:642. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00642. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33178131 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cognitive impairment and apolipoprotein A1 or apolipoprotein B levels is regulated by apolipoprotein E variant rs429358 in patients with chronic schizophrenia.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 16;13(12):16353-16366. doi: 10.18632/aging.203161. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34135129 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Obesity and Cognitive Function in Chinese Elderly Patients With Chronic Schizophrenia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 1;13:742474. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.742474. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35432207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jobe TH, Harrow M. Schizophrenia course, long-term outcome, recovery, and prognosis. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2010;19:220–225. doi: 10.1177/0963721410378034. - DOI
-
- Rezaee O, Saeede MM, Reza M, Akbarpour FA. Placebo-controlled trial of bupropion for improving the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health. 2012;4:1265–1275.
-
- Soštarič M, Zalar B. The overlap of cognitive impairment in depression and schizophrenia: a comparative study. Psychiatr Danub. 2011;23:251–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

