Burkholderia stabilis outbreak associated with contaminated commercially-available washing gloves, Switzerland, May 2015 to August 2016
- PMID: 29233255
- PMCID: PMC5727593
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.49.17-00213
Burkholderia stabilis outbreak associated with contaminated commercially-available washing gloves, Switzerland, May 2015 to August 2016
Abstract
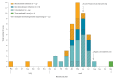
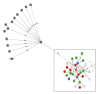
We describe an outbreak of Burkholderia stabilis associated with contaminated washing gloves, a commercially available Class I medical device. Triggered by an increase in Burkholderia cepacia complex (BCC) bacteremias and the detection of BCC in unopened packages of washing gloves, an ad hoc national outbreak committee comprising representatives of a public health organisation, a regulatory agency, and an expert association convened and commissioned an outbreak investigation. The investigation included retrospective case finding across Switzerland and whole genome sequencing (WGS) of isolates from cases and gloves. The investigation revealed that BCC were detected in clinical samples of 46 cases aged 17 to 91 years (33% females) from nine institutions between May 2015 and August 2016. Twenty-two isolates from case patients and 16 from washing gloves underwent WGS. All available outbreak isolates clustered within a span of < 19 differing alleles, while 13 unrelated clinical isolates differed by > 1,500 alleles. This BCC outbreak was rapidly identified, communicated, investigated and halted by an ad hoc collaboration of multiple stakeholders. WGS served as useful tool for confirming the source of the outbreak. This outbreak also highlights current regulatory limitations regarding Class I medical devices and the usefulness of a nationally coordinated outbreak response.
Keywords: Burkholderia cepacia complex; Burkholderia stabilis; medical device, whole genome sequencing; nationwide; outbreak.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European Commission (EC). Medical Devices: Guidance document. Classification of medical devices. Guidelines relating to the application of the Council Directive 93/42/EEC on medical devices. MEDDEV 2. 4/1 Rev. 9. Luxembourg: EC; June 2010. [Accessed 16 Sep 2016]. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/consumers/sectors/medical-devices/files/meddev/2_4_1...
-
- The Swiss Federal Council. Medical Devices Ordinance (MedDO) of 17 October 2001. Bern; the Swiss Federal Council; 1 Jan 2002. [Accessed 12 Dec 2016]. Available from: https://www.admin.ch/opc/en/classified-compilation/19995459/index.html
-
- European Commission. Council Directive 93/42/EEC of 14 June 1993 concerning medical devices. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. L169. 12 Jul 1993. Available from: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:1993L0042:...
-
- European Commission. The ‘Blue Guide’ on the implementation of EU products rules 2016. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. C272. 26 Jul 2016. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/DocsRoom/documents/12661/attachments/1/translations/...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
