Trichostatin A inhibits deacetylation of histone H3 and p53 by SIRT6
- PMID: 29233643
- PMCID: PMC5762261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.12.009
Trichostatin A inhibits deacetylation of histone H3 and p53 by SIRT6
Abstract
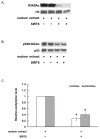
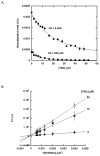
SIRT6 is an epigenetic modification enzyme that regulates gene transcription through its deacetylase activity. In addition to histone protein, SIRT6 also modify other proteins and enzymes, some of which are central players in metabolic reprogramming and aging process. Therefore, SIRT6 has emerged as a therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic disorder and age-related diseases. Here, we report that SIRT6 deacetylates lysine 382 of p53 in short synthetic peptide sequence and in full length p53. Further studies showed that the deacetylation of H3K9Ac and p53K382Ac are insensitive to nicotinamide inhibition, but are sensitive to trichostatin A (TSA) inhibition. Detailed kinetic analysis revealed that TSA competes with the peptide substrate for inhibition, and this inhibition is unique to SIRT6 in the sirtuin family. Taken together, this study not only suggests potential roles of SIRT6 in regulating apoptosis and stress resistance via direct deacetylation of p53, but also provides lead compound for the development of potent and selective SIRT6 inhibitors.
Keywords: Inhibition; NAD(+)-dependent deacetylation; Sirtuin.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Sauve AA, Wolberger C, Schramm VL, Boeke JD. The biochemistry of sirtuins. Annual review of biochemistry. 2006;75:435–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

