Ethnopharmacological Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Properties of Croton macrostachyus Hochst. Ex Delile: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 29234365
- PMCID: PMC5660826
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1694671
Ethnopharmacological Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Properties of Croton macrostachyus Hochst. Ex Delile: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
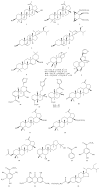
Croton macrostachyus is widely used as herbal medicine by the indigenous people of tropical Africa. The potential of C. macrostachyus as herbal medicine, the phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of its parts used as herbal medicines are reviewed. The extensive literature survey revealed that C. macrostachyus is traditionally used to treat or manage at least 81 human and animal diseases and ailments. The species is used as herbal medicine for diseases and ailments such as abdominal pains, cancer, gastrointestinal disorders, malaria, pneumonia, sexually transmitted infections, skin infections, typhoid, and wounds and as ethnoveterinary medicine. Multiple classes of phytochemicals such as alkaloids, amino acids, anthraquinones, carbohydrates, cardiac glycosides, coumarins, essential oil, fatty acids, flavonoids, phenolic compounds, phlobatannins, polyphenols, phytosteroides, saponins, sterols, tannins, terpenoids, unsaturated sterol, vitamin C, and withanoides have been isolated from the species. Pharmacological studies on C. macrostachyus indicate that it has a wide range of pharmacological activities such as anthelmintic, antibacterial, antimycobacterial, antidiarrhoeal, antifungal, anticonvulsant and sedative, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antileishmanial, antioxidant, antiplasmodial, and larvicidal effects. Croton macrostachyus has potential as a possible source of a wide range of pharmaceutical products for the treatment of a wide range of both human and animal diseases and ailments.
Figures
References
-
- Smith A. R. Euphorbaceae. In: Polhill R. M., editor. Flora of Tropical East Africa. Rotterdam, The Netherlands: A A Balkema; 1987. pp. 20–391.
-
- Gilbert M. G. Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea. In: Edwards S., Mesfin T., Hedberg I., editors. Euphorbiaceae. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Addis Ababa University; 1995. pp. 265–380.
-
- Wakjira K., Negash L. Germination responses of Croton macrostachyus (Euphorbiaceae) to various physico-chemical pretreatment conditions. South African Journal of Botany. 2013;87:76–83. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2013.03.012. - DOI
-
- Bekele-Tesemma A., Birnie A., Tengnäs B. Technical Handbook no. 5, Regional Soil Conservation Unit/SIDA. Nairobi, Kenya: Regional Soil Conservation Unit/SIDA; 1993. Useful trees and shrubs for ethiopia: identification, propagation and management for agricultural and pastoral communities.
-
- Hines D. A., Eckman K. Indigenous Multipurpose Trees for Tanzania: Uses and Economic Benefits to the People. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 1993.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources