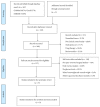
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Lifestyle Modification on Metabolic Control in Overweight Children
- PMID: 29234414
- PMCID: PMC5635284
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5681909
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Lifestyle Modification on Metabolic Control in Overweight Children
Abstract
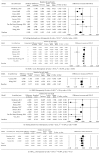
Childhood obesity is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. We aimed to determine the effects of lifestyle modification programs on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels in overweight children. We queried six relevant electronic databases and manually searched for studies published before December 2016. Overweight/obese children who underwent a lifestyle modification for more than 6 months were included. A total of 3923 children from eight randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. Compared with the control group, the lifestyle modification group had significantly lower FPG levels by 1.3 mg/dL. The mean differences were significantly decreased for both secondary outcomes; BMI z-score decreased by 0.16 units and insulin levels decreased by 2.4 mU/L. The metaregression showed that the follow-up duration was associated with FPG levels and BMI and insulin levels and half year is a suitable follow-up duration for this population. This study showed that lifestyle modification programs may be effective in reducing the FPG levels of overweight/obese children. Further high-quality RCTs with longer follow-up periods are needed to evaluate the long-term effect of this complementary approach for diabetes mellitus prevention on overweight/obese children.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
-
Treatment of overweight and obesity in children and youth: a systematic review and meta-analysis.CMAJ Open. 2015 Jan 13;3(1):E35-46. doi: 10.9778/cmajo.20140047. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. CMAJ Open. 2015. PMID: 25844368 Free PMC article.
-
[Metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese schoolchildren in Beijing].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Jun;45(6):417-21. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17880785 Chinese.
-
Impact of Game-Based Health Promotion Programs on Body Mass Index in Overweight/Obese Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Child Obes. 2018 Feb/Mar;14(2):67-80. doi: 10.1089/chi.2017.0250. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Child Obes. 2018. PMID: 29185787
Cited by
-
Fasting Plasma Glucose and Coronary Heart Disease in a Rural Population of North Henan, China.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Oct 10;2020:2348583. doi: 10.1155/2020/2348583. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33101438 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of pilot and small trials in meta-analyses of behavioral interventions: a meta-epidemiological study.Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 18;12(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02184-7. Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36803891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the underlying drivers of obesity in Africa: a scoping review protocol.BMJ Open. 2020 Nov 11;10(11):e040940. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040940. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 33177144 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lifestyle Modification Interventions to Prevent and Manage Child and Adolescent Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 24;12(8):2208. doi: 10.3390/nu12082208. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32722112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Childhood overweight and obesity: World Health Organization; 2015, Available from: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood/en/
-
- World Obesity Federation. World map of obesity in children 2015. Available from: http://www.worldobesity.org/?map=children.
-
- Chu N.-F., Pan W.-H. Prevalence of obesity and its comorbidities among schoolchildren in Taiwan. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2007;16(2):601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials