Removal of precursors and disinfection by-products (DBPs) by membrane filtration from water; a review
- PMID: 29234499
- PMCID: PMC5721515
- DOI: 10.1186/s40201-017-0285-z
Removal of precursors and disinfection by-products (DBPs) by membrane filtration from water; a review
Abstract
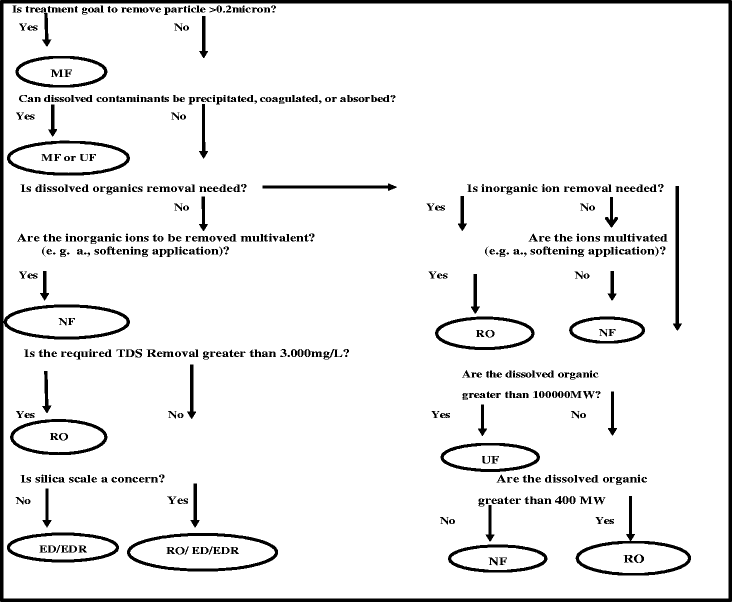
Disinfection by-products (DBPs) have heterogeneous structures which are suspected carcinogens as a result of reactions between NOMs (Natural Organic Matter) and oxidants/disinfectants such as chlorine. Because of variability in DBPs characteristics, eliminate completely from drinking water by single technique is impossible. The current article reviews removal of the precursors and DBPs by different membrane filtration methods such as Microfiltration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nanofiltration (NF) and Reverse Osmosis (RO) techniques. Also, we provide an overview of existing and potentially Membrane filtration techniques, highlight their strengths and drawbacks. MF membranes are a suitable alternative to remove suspended solids and colloidal materials. However, NOMs fractions are effectively removed by negatively charged UF membrane. RO can remove both organic and inorganic DBPs and precursors simultaneously. NF can be used to remove compounds from macromolecular size to multivalent ions.
Keywords: DBPs; Drinking water; HAA5; MF; Membrane technology; NF; NOMs; RO; THMs; UF.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Mansoori F., Ranandeh KL, ., Malakootian M,. Kinetics and Isothermic behavior of SiO2 nanoparticles in removal of humic acid from aqueous solutions: a case study on the Alavian dam in Maragheh City, Iran. 2014.
-
- Mansouri F, Kalankesh RL, Hasankhani H. The comparision of photo catalytic degredation of dissolved organic (DOC) from water by UV/TiO2 in the presence and absence of Iron ion. Global Nest Journal. 2016 Jun;18(2):392–401. PubMed PMID: WOS:000384530600017.
-
- Ghoochani M, Rastkari N, Heibati B, Ghozikali MG, Jeddi MZ, Fawell J, et al. Risk assessment of haloacetic acids in the water supply of Tehran, Iran. Water Science and Technology-Water Supply. 2017 Jul;17(4):958–965. PubMed PMID: WOS:000408713700006.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials