Association between vitamin D, oestradiol and interferon-gamma in female patients with inactive systemic lupus erythematosus: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 29235391
- PMCID: PMC5972245
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060517734686
Association between vitamin D, oestradiol and interferon-gamma in female patients with inactive systemic lupus erythematosus: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
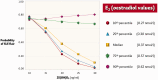
Objectives To investigate possible associations between 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3), oestradiol (E2) and IFN-gamma (IFNγ) in female patients with inactive systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Methods Female patients with inactive SLE and age-matched healthy controls were recruited into this cross-sectional study. Serum concentrations of 25(OH)D3, E2 and IFNγ were measured by radioimmunoassay with gamma-counters and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results 36 patients and 37 controls were enrolled. In patients with SLE, the concentration of 25(OH)D3 was lower and E2 was higher compared with controls. In vitamin D deficient (i.e., 25(OH)D3≤20 ng/ml) patients, IFNγ was 150% higher compared with patients with 25(OH)D3>20 ng/ml and controls. The concentration of E2 was higher in all patients compared with controls independently of the vitamin D level. A difference was found between patients and controls in the correlation of 25(OH)D3 with E2 and a positive correlation was found between E2 and IFNγ in all participants. Conclusions Our results suggest that E2 may have a strong modulating effect on vitamin D function which is significant only at low concentration of E2.
Keywords: Vitamin D; interferon-gamma; oestradiol; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
-
- Hagberg N, Rönnblom L. Systemic lupus erythematosus–a disease with a dysregulated type i interferon system. Scand J Immunol 2015; 82: 199–207. - PubMed
-
- Hertzog P Forster S andSamarajiwa S.. Systems biology of interferon responses. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2011; 31: 5–11. - PubMed
-
- Kidd P. Th1/Th2 balance: the hypothesis, its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Altern Med Rev 2003; 8: 223–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical