Nomogram for cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A simple self-assessed scale for individual risk of cirrhosis
- PMID: 29235488
- PMCID: PMC5727495
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17685-4
Nomogram for cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A simple self-assessed scale for individual risk of cirrhosis
Abstract
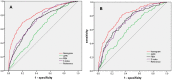
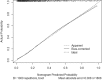
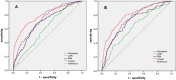
The aim of this retrospective study was to establish a simple self-assessed scale for individual risk of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. A total of 1808 consecutive patients were enrolled and analyzed. According to the results of multivariate logistic regression analysis, a simple nomogram was calculated for cirrhosis. The area under receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) were calculated to compare the diagnostic accuracy of nomogram with aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI), fibrosis index based on the four factors (FIB-4), and S index. The AUROCs of nomogram for cirrhosis were 0.807 (adjusted AUROC 0.876) in model group and 0.794 (adjusted AUROC0.866) in validation group. DeLong's test and Brier Score further demonstrated that nomogram was superior to APRI, FIB-4 and S index in both model group and validation group. The patients with nomogram <0.07 could be defined as low risk group with cirrhosis prevalence lower than 4.3% (17/397). The patients with nomogram >0.52 could be defined as high risk group with cirrhosis prevalence higher than 73.0% (119/163). In conclusion, as a self-assessed style, simple, non-invasive, economical, convenient, and repeatable scale, nomogram is suitable to serve as a massive health screening tool for cirrhosis in CHB patients and further external validation is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applicability of liver stiffness measurement based nomograms to the assessments of hepatitis B related significant fibrosis and cirrhosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Feb;489:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.11.029. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30471249
-
A Novel Prediction Model for Significant Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 8;2020:6839137. doi: 10.1155/2020/6839137. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32695818 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive diagnosis of significant liver inflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis B in the indeterminate phase.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2268497. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2268497. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37938933 Free PMC article.
-
Routine indexes for cirrhosis and significant fibrosis detection in patients with compensated chronic hepatitis B.Dig Liver Dis. 2019 Jan;51(1):127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Dig Liver Dis. 2019. PMID: 30076017
-
Non-invasive tests in prediction of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and comparison with post-antiviral treatment results.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr;37(2):152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2012.07.003. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23391746
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

