Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities
- PMID: 29236064
- PMCID: PMC5742848
- DOI: 10.3390/md15120388
Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities
Abstract
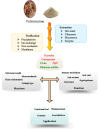
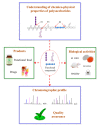
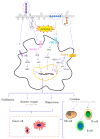
Marine algae have attracted a great deal of interest as excellent sources of nutrients. Polysaccharides are the main components in marine algae, hence a great deal of attention has been directed at isolation and characterization of marine algae polysaccharides because of their numerous health benefits. In this review, extraction and purification approaches and chemico-physical properties of marine algae polysaccharides (MAPs) are summarized. The biological activities, which include immunomodulatory, antitumor, antiviral, antioxidant, and hypolipidemic, are also discussed. Additionally, structure-function relationships are analyzed and summarized. MAPs' biological activities are closely correlated with their monosaccharide composition, molecular weights, linkage types, and chain conformation. In order to promote further exploitation and utilization of polysaccharides from marine algae for functional food and pharmaceutical areas, high efficiency, and low-cost polysaccharide extraction and purification methods, quality control, structure-function activity relationships, and specific mechanisms of MAPs activation need to be extensively investigated.
Keywords: characterization; extraction; marine algae; polysaccharide; structure-function relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rioux L.-E., Beaulieu L., Turgeon S.L. Seaweeds: A traditional ingredients for new gastronomic sensation. Food Hydrocoll. 2017;68:255–265. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.02.005. - DOI
-
- Mohamed S., Hashim S.N., Rahman H.A. Seaweeds: A sustainable functional food for complementary and alternative therapy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012;23:83–96. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.09.001. - DOI
-
- Hamed I., Özogul F., Özogul Y., Regenstein J.M. Marine bioactive compounds and their health benefits: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015;14:446–465. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12136. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

