Live attenuated influenza virus vaccine reduces virus shedding of newborn piglets in the presence of maternal antibody
- PMID: 29236357
- PMCID: PMC5907821
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12531
Live attenuated influenza virus vaccine reduces virus shedding of newborn piglets in the presence of maternal antibody
Abstract
Background: Influenza A virus in swine (IAV-S) causes an acute respiratory disease of swine which results in great economic losses in pig production. Major control strategies include the use of killed vaccines (KV) in breeding females to confer passive immunity to their offspring. A bivalent H1N1 and H3N2 NS1-truncated live attenuated IAV-S vaccine have recently become available, which showed promising results in young pigs.
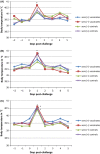
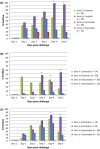
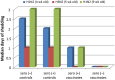
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of an intranasal vaccination of newborn pigs with or without maternally derived antibodies (MDA) on virus shedding (via nasal swabs tested by virus isolation).
Methods: The study was performed as intratracheal challenge experiments with either a heterologous H1N2 or H3N2 viruses.
Results and conclusion: The results of this study showed a significant decrease in the incidence and duration of shedding viable virus for vaccinated newborn piglets with or without MDA, providing strong evidence that intranasal vaccination is overcoming passively acquired maternal immunity. This study indicates that intranasal vaccination with a truncated NS1 live attenuated IAV-S vaccine of newborn piglets with maternal antibodies can be a valuable tool for reducing the prevalence of heterologous H1N2 and H3N2 IAV-S in pig herds.
Keywords: influenza A virus; live attenuated influenza virus vaccine; maternally derived antibodies; piglets; virus shedding.
© 2017 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Richt JA, García‐Sastre A. Attenuated influenza virus vaccines with modified NS1 proteins In: Compans R.W. and Orenstein W.A. (eds.), Vaccines for Pandemic Influenza, Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology 333. Springer‐Verlag, Berlin; 2009:177‐195. - PubMed
-
- Wacheck V, Egorov A, Groiss F, et al. A novel type of influenza vaccine: safety and immunogenicity of replication‐deficient influenza virus created by deletion of the interferon antagonist NS1. J Infect Dis. 2010;201:354‐362. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

