Origin and differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells after vaccination
- PMID: 29236685
- PMCID: PMC6037316
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24633
Origin and differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells after vaccination
Abstract
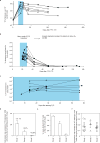
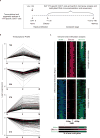
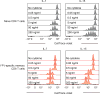
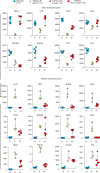
The differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells is not well understood. Here we address this issue using the live yellow fever virus (YFV) vaccine, which induces long-term immunity in humans. We used in vivo deuterium labelling to mark CD8 T cells that proliferated in response to the virus and then assessed cellular turnover and longevity by quantifying deuterium dilution kinetics in YFV-specific CD8 T cells using mass spectrometry. This longitudinal analysis showed that the memory pool originates from CD8 T cells that divided extensively during the first two weeks after infection and is maintained by quiescent cells that divide less than once every year (doubling time of over 450 days). Although these long-lived YFV-specific memory CD8 T cells did not express effector molecules, their epigenetic landscape resembled that of effector CD8 T cells. This open chromatin profile at effector genes was maintained in memory CD8 T cells isolated even a decade after vaccination, indicating that these cells retain an epigenetic fingerprint of their effector history and remain poised to respond rapidly upon re-exposure to the pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


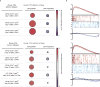
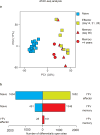

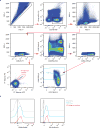
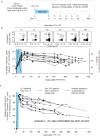


Comment in
-
The origins of memory T cells.Nature. 2017 Dec 21;552(7685):337-339. doi: 10.1038/d41586-017-08280-8. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29293221 No abstract available.
-
Heavy Water Shedding Light on Antigen-Specific T Cell Responses.Trends Immunol. 2018 Mar;39(3):170-172. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Trends Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29396015
References
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Lau LL, Jamieson BD, Somasundaram T, Ahmed R. Cytotoxic T-cell memory without antigen. Nature. 1994;369:648–652. - PubMed
-
- Nanan R, Rauch A, Kämpgen E, Niewiesk S, Kreth HW. A novel sensitive approach for frequency analysis of measles virus-specific memory T-lymphocytes in healthy adults with a childhood history of natural measles. J. Gen. Virol. 2000;81:1313–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

