ciRS-7 exonic sequence is embedded in a long non-coding RNA locus
- PMID: 29236709
- PMCID: PMC5745005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007114
ciRS-7 exonic sequence is embedded in a long non-coding RNA locus
Abstract
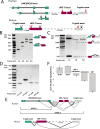
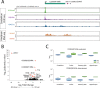
ciRS-7 is an intensely studied, highly expressed and conserved circRNA. Essentially nothing is known about its biogenesis, including the location of its promoter. A prevailing assumption has been that ciRS-7 is an exceptional circRNA because it is transcribed from a locus lacking any mature linear RNA transcripts of the same sense. To study the biogenesis of ciRS-7, we developed an algorithm to define its promoter and predicted that the human ciRS-7 promoter coincides with that of the long non-coding RNA, LINC00632. We validated this prediction using multiple orthogonal experimental assays. We also used computational approaches and experimental validation to establish that ciRS-7 exonic sequence is embedded in linear transcripts that are flanked by cryptic exons in both human and mouse. Together, this experimental and computational evidence generates a new model for regulation of this locus: (a) ciRS-7 is like other circRNAs, as it is spliced into linear transcripts; (b) expression of ciRS-7 is primarily determined by the chromatin state of LINC00632 promoters; (c) transcription and splicing factors sufficient for ciRS-7 biogenesis are expressed in cells that lack detectable ciRS-7 expression. These findings have significant implications for the study of the regulation and function of ciRS-7, and the analytic framework we developed to jointly analyze RNA-seq and ChIP-seq data reveal the potential for genome-wide discovery of important biological regulation missed in current reference annotations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO (2012) Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 7: e30733 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030733 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, et al. (1993) Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 73: 1019–1030. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90279-Y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, et al. (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 19: 141–157. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, et al. (1991) Scrambled exons. Cell 64: 607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90244-S - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee M-C, Barrett SP, Hogan GJ, et al. (2014) Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS ONE 9: e90859 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090859 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

