The Impact of Skin Problems on the Quality of Life in Patients Treated with Anticancer Agents: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 29237254
- PMCID: PMC6192901
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.435
The Impact of Skin Problems on the Quality of Life in Patients Treated with Anticancer Agents: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Purpose: Patients treated with anticancer agents often experience a variety of treatment-related skin problems, which can impair their quality of life.
Materials and methods: In this cross-sectional study, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and clinical information were evaluated in patients under active anticancer treatment using a questionnaire survey and their medical records review.
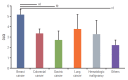
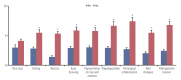
Results: Of 375 evaluated subjects with anticancer therapy, 136 (36.27%) and 114 (30.40%) were treated for breast cancer and colorectal cancer, respectively. We found that women, breast cancer, targeted agent use, and longer duration of anticancer therapy were associated with higher dermatology-specific quality of life distraction. In addition, itching, dry skin, easy bruising, pigmentation, papulopustules on face, periungual inflammation, nail changes, and palmoplantar lesions were associated with significantly higher DLQI scores. Periungual inflammation and palmoplantar lesions scored the highest DLQI.
Conclusion: We believe our findings can be helpful to clinicians in counseling and managing the patients undergoing anticancer therapy.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; Antineoplastic agents; Dermatology Life Quality Index; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Byun HJ, Lee HJ, Yang JI, Kim KH, Park KO, Park SM, et al. Daily skin care habits and the risk of skin eruptions and symptoms in cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1992–8. - PubMed
-
- Boone SL, Rademaker A, Liu D, Pfeiffer C, Mauro DJ, Lacouture ME. Impact and management of skin toxicity associated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy: survey results. Oncology. 2007;72:152–9. - PubMed
-
- Lacouture ME. The growing importance of skin toxicity in EGFR inhibitor therapy. Oncology (Williston Park) 2009;23:194. - PubMed
-
- Huang V, Anadkat M. Dermatologic manifestations of cytotoxic therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:401–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

