Delay in diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in low-and middle-income settings: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29237451
- PMCID: PMC5729407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-017-0551-y
Delay in diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in low-and middle-income settings: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
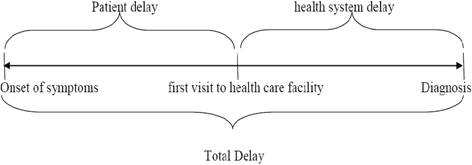
Background: Assessment of delays in seeking care and diagnosis of tuberculosis is essential to evaluate effectiveness of tuberculosis control programs, and identify programmatic impediments. Thus, this review of studies aimed to examine the extent of patient, health system, and total delays in diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in low- and middle- income countries.
Methods: It was done following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Electronic databases were searched to retrieve studies published from 2007 to 2015 including Pubmed central, Springer link, Hinari and Google scholar. Searching terms were pulmonary tuberculosis, health care seeking, health care seeking behavior, patient delay, diagnostic delay, health system delay, provider delay, and doctor delay. Retrieved studies were systematically reviewed and summarized using Comprehensive Meta-analysis software.
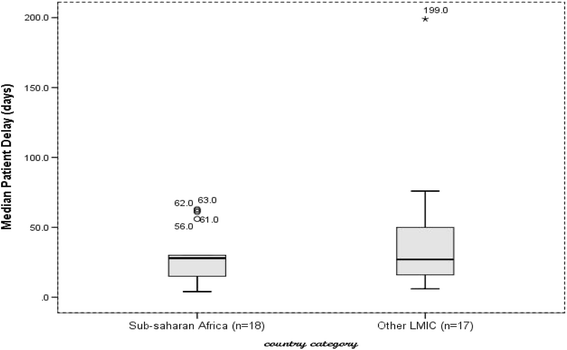
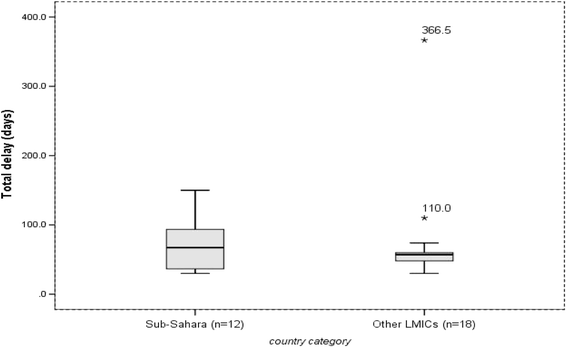
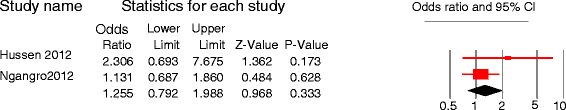
Results: Forty studies involving 18,975 patients qualified for systematic review, and 14 of them qualified for meta-analysis. The median diagnostic delay ranged from 30 to 366.5 days [IQR = 44-77.8], with a 4-199 days [IQR = 15-50] and 2-128.5 days [IQR = 12-34] due to patient and health system delays, respectively. The meta-analysis showed 42% of pulmonary tuberculosis patients delayed seeking care by a month or more; uneducated patients [pooled OR = 1.5, 95%CI = 1.1-1.9] and those who sought initial care from informal providers [pooled OR = 3, 95%CI = 2.3-3.9] had higher odds of patient delay.
Conclusion: Delay in diagnosis is still a major challenge of tuberculosis control and prevention programs in low- and middle- income settings. Efforts to develop new strategies for better case-finding using the existing systems and improving patients' care seeking behavior need to be intensified.
Keywords: Diagnosis delay; Health system; Patient delay; Pulmonary tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




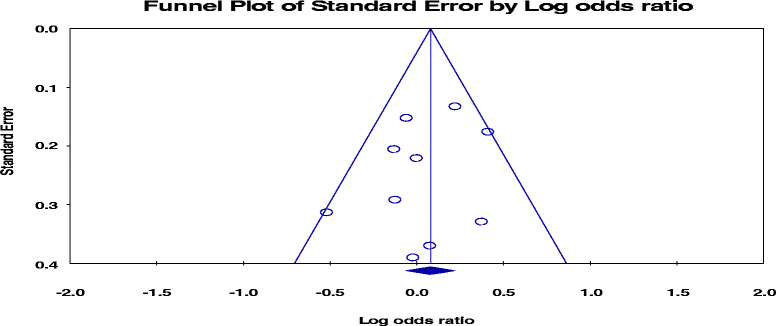



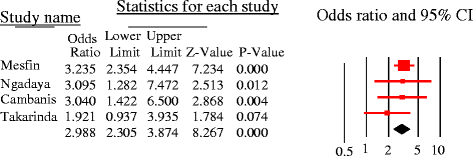

References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available at http://apps.who.int/iris.
-
- WHO. The global plan to stop TB 2011-2015: Transforming the fight towards elimination of tuberculosis. World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- WHO. Systematic screening for active tuberculosis: principles and recommendations. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Treatment of tuberculosis: guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

