Drug-induced Liver Injury Due to Lepidium meyenii (Maca) Medicinal Liquor
- PMID: 29237937
- PMCID: PMC5742932
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.220314
Drug-induced Liver Injury Due to Lepidium meyenii (Maca) Medicinal Liquor
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
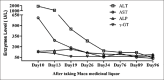
Figures
References
-
- Gonzales GF, Villaorduña L, Gasco M, Rubio J, Gonzales C. Maca (Lepidium meyenii walp), a review of its biological properties. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 2014;31:100–10. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Zhao Q, Wang L, Zhao M, Zhao B. Protective effect of polysaccharide from maca (Lepidium meyenii) on hep-G2 cells and alcoholic liver oxidative injury in mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;99:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.125. - PubMed
-
- Valentová K, Stejskal D, Bartek J, Dvorácková S, Kren V, Ulrichová J, et al. Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) in combination with silymarin as food supplements: In vivo safety assessment. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:1006–13. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.10.031. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical