circHIPK2-mediated σ-1R promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pulmonary fibroblasts exposed to silica
- PMID: 29238093
- PMCID: PMC5870587
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-017-0017-4
circHIPK2-mediated σ-1R promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pulmonary fibroblasts exposed to silica
Abstract
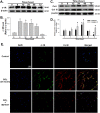
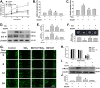
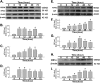
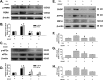
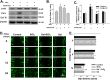
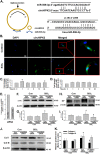
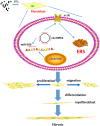
Silicosis is characterized by fibroblast accumulation and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix. Although the roles of SiO2-induced chemokines and cytokines released from alveolar macrophages have received significant attention, the direct effects of SiO2 on protein production and functional changes in pulmonary fibroblasts have been less extensively studied. Sigma-1 receptor, which has been associated with cell proliferation and migration in the central nervous system, is expressed in the lung, but its role in silicosis remains unknown. To elucidate the role of sigma-1 receptor in fibrosis induced by silica, both the upstream molecular mechanisms and the functional effects on cell proliferation and migration were investigated. Both molecular biological assays and pharmacological techniques, combined with functional experiments, such as migration and proliferation, were applied in human pulmonary fibroblasts from adults to analyze the molecular and functional changes induced by SiO2. SiO2 induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in association with enhanced expression of sigma-1 receptor. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promoted migration and proliferation of human pulmonary fibroblasts-adult exposed to SiO2, inducing the development of silicosis. Inhibition of sigma-1 receptor ameliorated endoplasmic reticulum stress and fibroblast functional changes induced by SiO2. circHIPK2 is involved in the regulation of sigma-1 receptor in human pulmonary fibroblasts-adult exposed to SiO2. Our study elucidated a link between SiO2-induced fibrosis and sigma-1 receptor signaling, thereby providing novel insight into the potential use of sigma-1 receptor/endoplasmic reticulum stress in the development of novel therapeutic strategies for silicosis treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest..
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of human pulmonary fibroblast-derived MCP-1 in cell activation and migration in experimental silicosis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;288(2):152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.07.002. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26163174
-
CircRNA-012091/PPP1R13B-mediated Lung Fibrotic Response in Silicosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Sep;61(3):380-391. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0017OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30908929
-
Silica-induced initiation of circular ZC3H4 RNA/ZC3H4 pathway promotes the pulmonary macrophage activation.FASEB J. 2018 Jun;32(6):3264-3277. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701118R. Epub 2018 Jan 22. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29401612
-
Silicon dioxide-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress of alveolar macrophages and its role on the formation of silicosis fibrosis: a review article.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Oct 28;12(6):1024-1033. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad099. eCollection 2023 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 38145097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted role of macrophage mitophagy in SiO2-induced pulmonary fibrosis: A brief review.J Appl Toxicol. 2024 Dec;44(12):1854-1867. doi: 10.1002/jat.4612. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Appl Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38644760 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs and their roles in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2024 Feb 6;25(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02716-2. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38321530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circHECTD1 promotes the silica-induced pulmonary endothelial-mesenchymal transition via HECTD1.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Mar 14;9(3):396. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0432-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29540674 Free PMC article.
-
Sp1-Mediated circRNA circHipk2 Regulates Myogenesis by Targeting Ribosomal Protein Rpl7.Genes (Basel). 2021 May 8;12(5):696. doi: 10.3390/genes12050696. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066653 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins in Fibrosis: Complex Roles Beyond Conventional Understanding.Research (Wash D C). 2022 Oct 3;2022:9891689. doi: 10.34133/2022/9891689. eCollection 2022. Research (Wash D C). 2022. PMID: 36299447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Natural Products through Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress on Attenuation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 May 17;18:1627-1650. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S388920. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38774483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

