Efficacy comparison of intramedullary nails, locking plates and conservative treatment for displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly
- PMID: 29238180
- PMCID: PMC5713686
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S144084
Efficacy comparison of intramedullary nails, locking plates and conservative treatment for displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly
Abstract
Purpose: The incidence of proximal humeral fractures is high in the elderly, and the superior management of these fractures remains a controversy. The study aims to compare clinical outcomes of intramedullary nails, locking plates and conservative treatment for the management of displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly.
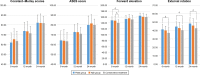
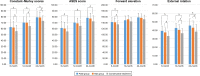
Patients and methods: In this prospective study, a total of 198 patients with 2- or 3-part proximal humeral fractures who received fixation of locking plates or intramedullary nails or conservative treatment were included. The primary outcome was the 24-month Constant-Murley score. The secondary outcomes included the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) scores, the visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, shoulder range of motion and complication rate.
Results: There were no statistically significant differences in the Constant-Murley scores and ASES scores among the plate group, the nail group and the conservative group for 2-part fractures. For 3-part fractures, Constant-Murley scores and ASES scores were lower in the conservative group compared with those in the plate group and the nail group. Besides, the conservative group showed a significantly lower external rotation during follow-ups. The complication rate was comparable among the plate group, the nail group and the conservative group for both 2-part and 3-part fractures.
Conclusion: Similar satisfactory functional outcomes can be achieved with the locking plates, intramedullary nails or conservative treatment for 2-part proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. The advantages in functional outcomes favor locking plates and intramedullary nails in the management of 3-part proximal humeral fractures.
Keywords: conservative treatment; intramedullary nails; locking plates; proximal humeral fractures; the elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Hak DJ, Mauffrey C, Hake M, Hammerberg EM, Stahel PF. Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: current diagnostic and treatment strategies. Orthopedics. 2015;38(4):247–251. - PubMed
-
- Maier D, Jäger M, Strohm PC, Südkamp NP. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures – a review of current concepts enlightened by basic principles. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012;79(4):307–316. - PubMed
-
- Hintermann B, Trouillier HH, Schafer D. Rigid internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus in older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(8):1107–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

