Renal Function During an Open-Label Prospective Observational Trial of Sitagliptin in Patients With Diabetes: A Sub-Analysis of the JAMP Study
- PMID: 29238432
- PMCID: PMC5722043
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr3225w
Renal Function During an Open-Label Prospective Observational Trial of Sitagliptin in Patients With Diabetes: A Sub-Analysis of the JAMP Study
Abstract
Background: The aim of the study was to determine the effects of sitagliptin on renal function in a diabetic population including patients with normal renal function.
Methods: We analyzed the association between 12-month, 50 mg/day sitagliptin and renal function in outpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and poor blood glucose control in a subset of patients in the larger Januvia Multicenter Prospective Trial in Type 2 Diabetes observational study. Stratified analyses of changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) were performed. Factors associated with changes in eGFR at 3 months were examined by multivariate regression analysis.
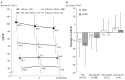
Results: Of the 779 patients enrolled, 585 were followed up for 12 months. eGFR decreased significantly from baseline at 3 and 12 months in patients with a baseline eGFR of ≥ 90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and in those with a baseline eGFR of ≥ 60 to < 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Conversely, eGFR tended to increase at 3 and 12 months in patients with a baseline eGFR of ≥ 45 to < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and in those with a baseline eGFR of ≥ 30 to < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. UACR decreased significantly (-21.6 (-46.8, 7.8)) at 3 months in patients with a baseline UACR of ≥ 30 mg/g Cre. Multivariate regression analysis of factors associated with changes in eGFR at 3 months revealed that higher baseline eGFR and greater decline in UACR were associated with more conspicuous decreases in eGFR.
Conclusions: In this group of diabetic patients receiving sitagliptin, eGFR declined in patients with high baseline eGFR, but not in those with a low baseline eGFR.
Keywords: DPP-4 inhibitor; JAMP; Prospective observational study; Renal function; Sitagliptin.
Conflict of interest statement
Hiroshi Sakura received honoraria from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation and research grant from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Herman GA, Bergman A, Stevens C, Kotey P, Yi B, Zhao P, Dietrich B. et al. Effect of single oral doses of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, on incretin and plasma glucose levels after an oral glucose tolerance test in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(11):4612–4619. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kashiwagi A, Kadowaki T, Tajima N, Nonaka K, Taniguchi T, Nishii M, Ferreira JC. et al. Sitagliptin added to treatment with ongoing pioglitazone for up to 52 weeks improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2011;2(5):381–390. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2011.00120.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
