Insulin-like growth factor 2 expression in prostate cancer is regulated by promoter-specific methylation
- PMID: 29239100
- PMCID: PMC5792735
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12164
Insulin-like growth factor 2 expression in prostate cancer is regulated by promoter-specific methylation
Abstract
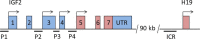
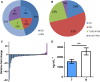
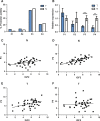
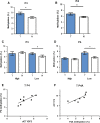
Deregulation of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis and dysbalance of components of the IGF system as potential therapeutic targets have been described in different tumor types. IGF2 is a major embryonic growth factor and an important activator of IGF signaling. It is regulated by imprinting in a development- and tissue-dependent manner and has been implicated in a broad range of malignancies including prostate cancer (PCa). Loss of imprinting (LOI) usually results in bi-allelic gene expression and increased levels of IGF2. However, the regulatory mechanisms and the pathophysiological impact of altered IGF2 expression in PCa remain elusive. Here, we show that in contrast to many other tumors, IGF2 mRNA and protein levels were decreased in 80% of PCa in comparison with non-neoplastic adjacent prostate and were independent of LOI status. Instead, IGF2 expression in both tumors and adjacent prostate depended on preferential usage of the IGF2 promoters P3 and P4. Decreased IGF2 expression in tumors was strongly related to hypermethylation of these two promoters. Methylation of the A region in promoter P4 correlated specifically with IGF2 expression in the 20% of PCa where IGF2 was higher in tumors than in adjacent prostate. We conclude that IGF2 is downregulated in most PCa and may be particularly relevant during early stages of tumor development or during chemotherapy and androgen deprivation. PCa differs from other tumors in that IGF2 expression is mainly regulated through methylation of promoter-specific and not by imprinting. Targeting of promoter-specific regions may have relevance for the adjuvant treatment of PCa.
Keywords: IGF2; imprinting; promoter methylation; prostate cancer; targeted therapy.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Belharazem D, Magdeburg J, Berton AK, Beissbarth L, Sauer C, Sticht C, Marx A, Hofheinz R, Post S, Kienle P et al (2016) Carcinoma of the colon and rectum with deregulation of insulin‐like growth factor 2 signaling: clinical and molecular implications. J Gastroenterol 51, 971–984. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

