SERPINH1 overexpression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: association with poor clinical outcome and its potential as a novel prognostic marker
- PMID: 29239102
- PMCID: PMC5783852
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13495
SERPINH1 overexpression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: association with poor clinical outcome and its potential as a novel prognostic marker
Abstract
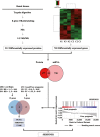
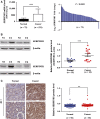
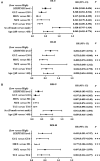
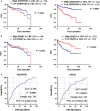
Precision therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) requires molecular biomarkers ascertaining disease prognosis. In this study, we performed integrated proteomic and transcriptomic screening in all four tumour-node-metastasis stages of ccRCC and adjacent normal tissues (n = 18) to investigate differentially expressed genes. Most identified differentially expressed genes revealed a strong association with transforming growth factor-β level and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process. Of them, Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1) revealed the strongest association with poor prognosis and regulation on the expression levels of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers. Subsequently, two independent sets (n = 532 and 105) verified the high level of SERPINH1 in ccRCC tissues and its association with reduced overall survival and disease-free survival in all tumour-node-metastasis stages and patients with von Hippel-Lindau wild-type (VHL-WT). SERPINH1 was an independent predictor of poor overall survival (hazard ratio 0.696 for all patients) and disease-free survival (hazard ratio 0.433 for all patients and 0.362 for patients with VHL-WT) in ccRCC. We have thus shown for the first time that SERPINH1 is an independent precision predictor for unfavourable prognosis in ccRCC. This could assist in identifying patients who need early aggressive management and deepen our understanding of the pathogenesis of VHL-WT ccRCC.
Keywords: SERPINH1/HSP47; prognostic marker; proteomics; renal cancer; transcriptomics.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- White NM, Yousef GM. Translating molecular signatures of renal cell carcinoma into clinical practice. J Urol. 2011; 186: 9–11. - PubMed
-
- Feldkoren B, Hutchinson R, Rapaport Y, et al Integrin signaling potentiates transforming growth factor‐beta 1 (TGF‐beta1) dependent down‐regulation of E‐Cadherin expression ‐ Important implications for epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal cell carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 2017; 355: 57–66. - PubMed
-
- Haddad AQ, Luo JH, Krabbe LM, et al Prognostic value of tissue‐based biomarker signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2017; 119: 741–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

