Oxymatrine inhibits non-small cell lung cancer via suppression of EGFR signaling pathway
- PMID: 29239135
- PMCID: PMC5773973
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1269
Oxymatrine inhibits non-small cell lung cancer via suppression of EGFR signaling pathway
Abstract
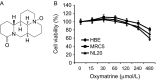
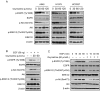
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays a crucial role in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis. In this study, oxymatrine was identified as an EGFR signaling pathway inhibitor in NSCLC. Oxymatrine inhibited anchorage-dependent and independent growth of NSCLC cell lines but had no cytotoxicity in normal lung cells. We found that exposure to oxymatrine not only suppressed the activity of wild-type EGFR but also inhibited the activation of exon 19 deletion and L858R/T790M mutated EGFR. Flow cytometry analysis suggested that oxymatrine-induced cell cycle G0/G1 arrest was dependent on EGFR-Akt signaling. Exogenous overexpression of Myr-Akt rescued cyclin D1 expression in HCC827 cells. Moreover, oxymatrine prominently suppressed tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Thus, oxymatrine appears to be a novel therapeutic agent for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: Akt; cyclin D1; epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; oxymatrine.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel, R. , Naishadham D., and Jemal A.. 2013. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis, C. E. , Lin C. C., Mariotto A. B., Siegel R. L., Stein K. D., Kramer J. L., et al. 2014. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 64:252–271. - PubMed
-
- Thomas, A. , Liu S. V., Subramaniam D. S., and Giaccone G.. 2015. Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to histological and molecular subtypes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 12:511–526. - PubMed
-
- Rosell, R. , and Karachaliou N.. 2015. Lung cancer in 2014: optimizing lung cancer treatment approaches. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 12:75–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

