Switch from tenofovir disoproxil fumarate combination to dolutegravir with rilpivirine improves parameters of bone health
- PMID: 29239893
- PMCID: PMC5802259
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001725
Switch from tenofovir disoproxil fumarate combination to dolutegravir with rilpivirine improves parameters of bone health
Abstract
Objective: Bone mineral density (BMD) loss, a risk factor for osteoporosis, has been attributed to HIV infection and antiretroviral therapy (ART), including regimens containing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Design: Study 202094 is an open-label, parallel-group, sub-study of the phase III SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 studies (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT02478632).
Methods: HIV-1-infected adults with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/ml who received ART containing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for at least 6 months were randomized to receive dolutegravir with rilpivirine or continue current ART regimen. Total hip and lumbar spine BMD were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans. The primary endpoint was percentage change from baseline in total hip BMD.
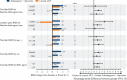
Results: DXA scans were evaluable for 81 participants at baseline and Week 48. Percentage increase in total hip BMD was significantly greater in participants who switched to dolutegravir with rilpivirine (1.34%) compared with participants who continued current ART (0.05%; treatment difference, +1.29%; 95% CI 0.27-2.31; P = 0.014). Lumbar spine BMD significantly increased in the dolutegravir with rilpivirine group by 1.46% (95% CI 0.65-2.28) compared with 0.15% (95% CI -0.79 to 1.09) in the current ART group (treatment difference, 1.32; 95% CI 0.07-2.57; P = 0.039). Participants in the dolutegravir with rilpivirine group experienced significantly greater reductions in bone formation and resorption biomarkers compared with the current ART group.
Conclusion: Switch to dolutegravir with rilpivirine was associated with significant improvement in BMD and bone turnover markers compared with tenofovir-based three-drug regimens, providing a robust option for preserving bone health while continuing suppressive ART.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02478632 NCT02429791 NCT02422797.
Figures
References
-
- Rivas P, Gorgolas M, Garcia-Delgado R, Diaz-Curiel M, Goyenechea A, Fernandez-Guerrero ML. Evolution of bone mineral density in AIDS patients on treatment with zidovudine/lamivudine plus abacavir or lopinavir/ritonavir. HIV Med 2008; 9:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Zhao H, Goetz MB. Complications of HIV infection in an ageing population: challenges in managing older patients on long-term combination antiretroviral therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66:1210–1214. - PubMed
-
- Hoy J, Young B. Do people with HIV infection have a higher risk of fracture compared with those without HIV infection?. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 2016; 11:301–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical