MAP kinases associate with high molecular weight multiprotein complexes
- PMID: 29240956
- PMCID: PMC5853780
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx424
MAP kinases associate with high molecular weight multiprotein complexes
Abstract
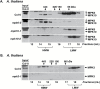
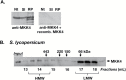
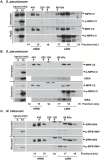
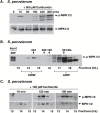
Plant responses to the environment and developmental processes are mediated by a complex signaling network. The Arabidopsis thaliana mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) MPK3 and MPK6 and their orthologs in other plants are shared signal transducers that respond to many developmental and environmental signals and thus represent highly connected hubs in the cellular signaling network. In animals, specific MAPK signaling complexes are assembled which enable input-specific protein-protein interactions and thus specific signaling outcomes. In plants, not much is known about such signaling complexes. Here, we report that MPK3, MPK6, and MPK10 orthologs in tomato, tobacco, and Arabidopsis as well as tomato MAPK kinase 4 (MKK4) associate with high molecular weight (~250-550 kDa) multiprotein complexes. Elicitation by the defense-associated peptides flg22 and systemin resulted in phosphorylation and activation of the monomeric MAPKs, whereas the complex-associated MAPKs remained unphosphorylated and inactive. In contrast, treatment of tomato cells with a phosphatase inhibitor resulted in association of phosphorylated MPK1/2 with the complex. These results demonstrate that plant MAPKs and MAPKKs dynamically assemble into stable multiprotein complexes and this may depend on their phosphorylation status. Identification of the constituents of these multiprotein complexes promises a deeper understanding of signaling dynamics.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; MAP kinase signaling; MAPK; MAPKK; multiprotein complex; phosphorylation; scaffold; signal transduction; size-exclusion chromatography; tomato.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, et al. . 2003. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Andreasson E, Ellis B. 2010. Convergence and specificity in the Arabidopsis MAPK nexus. Trends in Plant Science 15, 106–113. - PubMed
-
- Bartels S, González Besteiro MA, Lang D, Ulm R. 2010. Emerging functions for plant MAP kinase phosphatases. Trends in Plant Science 15, 322–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

