Body fluid status assessment by bio-impedance analysis in patients presenting to the emergency department with dyspnea
- PMID: 29241303
- PMCID: PMC6129632
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.358
Body fluid status assessment by bio-impedance analysis in patients presenting to the emergency department with dyspnea
Abstract
Background/aims: Fluid retention occurs in patients with heart failure, accounting for dyspnea. We investigated the diagnostic implication of body fluid status, assessed by bio-impedance analysis (BIA), in acute heart failure (AHF) among patients who presented with dyspnea.
Methods: A total of 100 patients who presented with dyspnea and suspected with AHF were analyzed in this study. We enrolled 50 AHF and 50 non-AHF patients discriminated through echocardiographic analysis and Framingham criteria and were matched by age and sex. Body composition was analyzed using a multifrequency BIA.
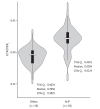
Results: AHF patients demonstrated higher extracellular water (ECW)/total body water (TBW) compared with non-AHF patients (0.412 ± 0.017 vs. 0.388 ± 0.023, p < 0.001). A significant difference of ECW/TBW between AHF patients and nonAHF patients was noted when the upper extremities, trunk, and lower extremities were analyzed (all p < 0.001, respectively). ECW/TBW was not different between patients with reduced ejection fraction (EF) and preserved EF along body compartments. The best cut-off value to predict AHF was > 0.412 at lower extremities with sensitivity and specificity of 0.780 and 0.960. The ECW/TBW of the lower extremities (ECW/TBWL) was correlated with log B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels (r = 0.603, p < 0.001) and also improved the net reclassification improvement and integrated discriminated improvement when added to log BNP level. Multivariate analysis revealed that ECW/TBWL > 0.412 had an independent association with AHF patients (p = 0.011).
Conclusion: The ECW/TBWL was higher in patients with dyspnea caused by AHF than their counterparts and demonstrated an independent diagnostic implication. It may be a promising marker to diagnose AHF at bedside.
Keywords: Dyspnea; Electric impedance; Heart failure; Natriuretic peptide, brain.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Schrier RW. Role of diminished renal function in cardiovascular mortality: marker or pathogenetic factor? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Cotter G, Metra M, Milo-Cotter O, Dittrich HC, Gheorghiade M. Fluid overload in acute heart failure: re-distribution and other mechanisms beyond fluid accumulation. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008;10:165–169. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18:891–975. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:e147–e239. - PubMed
-
- Drazner MH, Rame JE, Stevenson LW, Dries DL. Prognostic importance of elevated jugular venous pressure and a third heart sound in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:574–581. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
