Hybrid splicing minigene and antisense oligonucleotides as efficient tools to determine functional protein/RNA interactions
- PMID: 29242583
- PMCID: PMC5730568
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17816-x
Hybrid splicing minigene and antisense oligonucleotides as efficient tools to determine functional protein/RNA interactions
Abstract
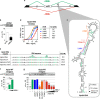
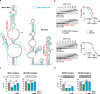
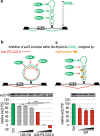
Alternative splicing is a complex process that provides a high diversity of proteins from a limited number of protein-coding genes. It is governed by multiple regulatory factors, including RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), that bind to specific RNA sequences embedded in a specific structure. The ability to predict RNA-binding regions recognized by RBPs using whole-transcriptome approaches can deliver a multitude of data, including false-positive hits. Therefore, validation of the global results is indispensable. Here, we report the development of an efficient and rapid approach based on a modular hybrid minigene combined with antisense oligonucleotides to enable verification of functional RBP-binding sites within intronic and exonic sequences of regulated pre-mRNA. This approach also provides valuable information regarding the regulatory properties of pre-mRNA, including the RNA secondary structure context. We also show that the developed approach can be used to effectively identify or better characterize the inhibitory properties of potential therapeutic agents for myotonic dystrophy, which is caused by sequestration of specific RBPs, known as muscleblind-like proteins, by mutated RNA with expanded CUG repeats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

