Subcutaneous tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: findings from the common-framework phase 4 study programme TOZURA conducted in 22 countries
- PMID: 29244149
- PMCID: PMC5850727
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex443
Subcutaneous tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: findings from the common-framework phase 4 study programme TOZURA conducted in 22 countries
Erratum in
-
Subcutaneous tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: findings from the common-framework phase 4 study programme TOZURA conducted in 22 countries.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018 Jun 1;57(6):1129. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key116. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 29635639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this pooled analysis of the TOZURA study programme was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous tocilizumab (TCZ-SC) as monotherapy or in combination with conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) in patients with moderate to severe RA who had an inadequate response to csDMARD or anti-TNF agent therapy or who were MTX naïve.
Methods: TOZURA is a multinational, open-label, single-arm, common-framework, phase 4 study programme (11 protocols, 22 countries). Patients received TCZ-SC 162 mg each week for ⩾24 weeks, administered at the investigator's discretion, as monotherapy or in combination with a csDMARD. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity were evaluated; propensity score-based matching was used for between-group comparisons.
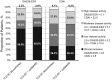
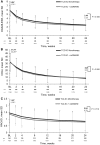
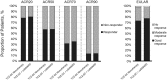
Results: Of 1804 patients, 353 (19.6%) received monotherapy and 1451 (80.4%) received combination therapy. The 28-joint DAS using ESR (DAS28-ESR) in both groups decreased significantly from baseline to week 24 (mean change: monotherapy -3.40, combination therapy -3.46), with no significant difference between groups (P = 0.46). The proportion of patients who achieved DAS28-ESR or Clinical Disease Activity Index remission or ACR 20/50/70/90 responses was similar between groups. Overall, 13.9% of patients withdrew-6.2% for safety reasons and 1.6% for insufficient therapeutic response; 5.8% of patients experienced one or more serious adverse events [14.6/100 patient-years (PY)]; six deaths occurred (0.64/100 PY).
Conclusion: In a common framework of 11 studies in 22 countries, this phase 4 study programme confirmed TCZ-SC's known efficacy and safety profile with comparable effects as monotherapy and in combination with csDMARDs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (http://www.clinicaltrials.gov) NCT01941940, NCT01941095, NCT01951170, NCT01987479, NCT01988012, NCT01995201, NCT02001987, NCT02011334, NCT02031471, NCT02046603 and NCT02046616.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Kazusa DNA Research Institute.
Figures
References
-
- Eulenfeld R, Dittrich A, Khouri C. et al. Interleukin-6 signalling: more than Jaks and STATs. Eur J Cell Biol 2012;91:486–95. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A. et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008;371:987–97. - PubMed
-
- Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL. et al. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:2968–80. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP. et al. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:1516–23. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

