The GDNF Family: A Role in Cancer?
- PMID: 29245123
- PMCID: PMC5730419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.10.010
The GDNF Family: A Role in Cancer?
Abstract
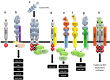
The glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of ligands (GFLs) comprising of GDNF, neurturin, artemin, and persephin plays an important role in the development and maintenance of the central and peripheral nervous system, renal morphogenesis, and spermatogenesis. Here we review our current understanding of GFL biology, and supported by recent progress in the area, we examine their emerging role in endocrine-related and other non-hormone-dependent solid neoplasms. The ability of GFLs to elicit actions that resemble those perturbed in an oncogenic phenotype, alongside mounting evidence of GFL involvement in tumor progression, presents novel opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Holm L, Hätinen T. Evolution of the GDNF family ligands and receptors. Brain Behav Evol. 2006;68(3):181–190. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3(5):383–394. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Titievsky A, Saarma M. GDNF family neurotrophic factor signaling: four masters, one servant? Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;13(5):313–325. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto H. Regulation of neural development by glial cell line–derived neurotrophic factor family ligands. Anat Sci Int. 2005;80(1):42–52. - PubMed
-
- Rangasamy SB, Soderstrom K, Bakay RA, Kordower JH. Neurotrophic factor therapy for Parkinson's disease. Prog Brain Res. 2010;184:237–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

