Higher efficacy of direct hemoperfusion using coated activated-charcoal column for disopyramide poisoning: A case report
- PMID: 29245231
- PMCID: PMC5728846
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008755
Higher efficacy of direct hemoperfusion using coated activated-charcoal column for disopyramide poisoning: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Cases of severe disopyramide poisoning are rare and few have been reported. We report a case in which activated-charcoal column hemoperfusion was dramatically effective for life-threatening disopyramide poisoning.
Patient concerns: A teenage girl who had overdosed on disopyramide (total dose, 4950 mg) was brought to our hospital. She was resuscitated from short period cardiopulmonary arrest and subsequently showed severe cardiogenic shock and ventricular arrhythmia.
Diagnoses: Disopyramide poisoning (self-evident).
Interventions: As hemodynamics remained unstable after providing percutaneous cardiopulmonary support and intra-aortic balloon pumping, we attempted direct hemoperfusion using a coated activated-charcoal hemoperfusion column.
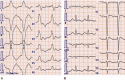
Outcomes: Hemodynamics including electrocardiography and serum disopyramide concentration were dramatically improved, and the patient was ambulatory by hospital day 14.
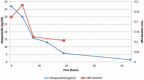
Lessons: Because disopyramide has low molecular weight and a small distribution volume, blood purification is considered to be the most effective therapy. We selected direct hemoperfusion for relatively high protein-binding rate. In fact, clinical status was dramatically improved, and the calculated half-life of the direct hemoperfusion phase was the shortest of all phases. In cases of severe or life-threatening disopyramide poisoning, blood purification therapy including direct hemoperfusion using a coated activated-charcoal column should be performed.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) Investigators. Preliminary report: effect of encainide and flecainide on mortality in a randomized trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1989;321:406–12. - PubMed
-
- Echt DS, Liebson PR, Mitchell LB, et al. Mortality and morbidity in patients receiving encainide, flecainide, or placebo: the cardiac arrhythmia suppression trial. N Engl J Med 1991;324:781–8. - PubMed
-
- Elsevier Inc., Winchester JF, Harbord NB, Feinfeld DA. Nissenson AR, Fine RN. Treatment of poisoning with extracorporeal methods. Handbook of Dialysis Therapy 4th ed.2008;1507–21. CHAPTER 108.
-
- Disopyramide: drug information. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate. Waltham, MA. (Accessed on Jun 14, 2015, Topic 9378 Version 124.0).
-
- Garella S. Extracorporeal techniques in the treatment of exogenous intoxications. Kidney Int 1988;33:735–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

