Refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body after treatment by balloon kyphoplasty: Three cases report
- PMID: 29245267
- PMCID: PMC5728882
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008961
Refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body after treatment by balloon kyphoplasty: Three cases report
Abstract
Rationale: Balloon kyphoplasty is a widely accepted treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) with good results and a low risk for complications. A refracture of previously treated vertebra is a relatively rare condition.
Patient concerns: We reported our 3 cases and reviewed all relevant literatures of 11 cases with refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body after kyphoplasty.
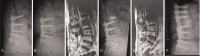
Diagnoses: Follow-up radiographs or magnetic resonance imaging examination confirmed refractures of previously treated vertebrae after kyphoplasty.
Interventions: One patient with 1 refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body after kyphoplasty was treated conservatively, but the other 2 patients were treated surgically because of multiple vertebral fractures or neurological deficits.
Outcomes: The average age of the patients was 76.8 years (range, 63-86 years). All the patients had severe osteoporosis with a mean T-score of -3.46 (range -5.0 to -3.0). The sites of refractures are in the lumbar and thoracolumbar regions. Severe osteoporosis, the presence of intravertebral cleft, and a solid lump injection pattern of polymethylmethacrylate would result in insufficient strengthening effects of cement augmentation and therefore increased the likelihood of refractures of the kyphoplasty vertibrae.
Lessons: Patients with OVCFs and intravertebral cleft who did not obtain complete pain-relief at the treated vertebral level after kyphoplasty should be strictly followed up. Early finding of this condition and rapid intervention might contribute to avoiding the occurrence of the cemented vertebral refracture after kyphoplasty. Conservative treatments such as back brace and antiosteoporotic medications were strongly recommended.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Du J, Li X, Lin X. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: two-year follow-up in a prospective controlled study. Acta Orthop Belg 2014;80:477–86. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Yang H, Tang T, et al. Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: twelve-month follow-up in a prospective nonrandomized comparative study. J Spinal Disord Tech 2012;25:142–9. - PubMed
-
- Rousing R, Hansen KL, Andersen MO, et al. Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:478–82. - PubMed
-
- Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Meirhaeghe JV, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373:1016–24. - PubMed
-
- Chiang CK, Wang YH, Yang CY, et al. Prophylactic vertebroplasty may reduce the risk of adjacent intact vertebra from fatigue injury an ex vivo biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:356–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

