Optic Pathway Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1
- PMID: 29246098
- PMCID: PMC5739070
- DOI: 10.1177/0883073817739509
Optic Pathway Gliomas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Abstract
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is one of the most common brain tumor predisposition syndromes, in which affected children are prone to the development of low-grade gliomas. While NF1-associated gliomas can be found in several brain regions, the majority arise in the optic nerves, chiasm, tracts, and radiations (optic pathway gliomas; OPGs). Owing to their location, 35-50% of affected children present with reduced visual acuity. Unfortunately, despite tumor stabilization following chemotherapy, vision does not improve in most children. For this reasons, more effective therapies are being sought that reflect a deeper understanding of the NF1 gene and the use of authenticated Nf1 genetically-engineered mouse strains. The implementation of these models for drug discovery and validation has galvanized molecularly-targeted clinical trials in children with NF1-OPG. Future research focused on defining the cellular and molecular factors that underlie optic glioma development and progression also has the potential to provide personalized risk assessment strategies for this pediatric population.
Keywords: RAS; astrocytoma; low-grade glioma; pilocytic; precision medicine; vision.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
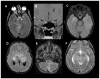
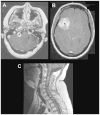

References
-
- Rasmussen SA, Friedman JM. NF1 gene and neurofibromatosis 1. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151(1):33–40. - PubMed
-
- Hirbe AC, Gutmann DH. Neurofibromatosis type 1: a multidisciplinary approach to care. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(8):834–43. - PubMed
-
- Gutmann DH, Rasmussen SA, Wolkenstein P, et al. Gliomas presenting after age 10 in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) Neurology. 2002;59(5):759–61. - PubMed
-
- Guillamo JS, Creange A, Kalifa C, et al. Prognostic factors of CNS tumours in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1): a retrospective study of 104 patients. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 1):152–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

