Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29246246
- PMCID: PMC5732365
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-017-0320-4
Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
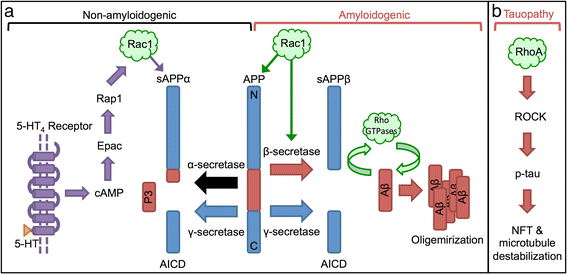
The progress we have made in understanding Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis has led to the identification of several novel pathways and potential therapeutic targets. Rho GTPases have been implicated as critical components in AD pathogenesis, but their various functions and interactions make understanding their complex signaling challenging to study. Recent advancements in both the field of AD and Rho GTPase drug development provide novel tools for the elucidation of Rho GTPases as a viable target for AD. Herein, we summarize the fluctuating activity of Rho GTPases in various stages of AD pathogenesis and in several in vitro and in vivo AD models. We also review the current pharmacological tools such as NSAIDs, RhoA/ROCK, Rac1, and Cdc42 inhibitors used to target Rho GTPases and their use in AD-related studies. Finally, we summarize the behavioral modifications following Rho GTPase modulation in several AD mouse models. As key regulators of several AD-related signals, Rho GTPases have been studied as targets in AD. However, a consensus has yet to be reached regarding the stage at which targeting Rho GTPases would be the most beneficial. The studies discussed herein emphasize the critical role of Rho GTPases and the benefits of their modulation in AD.
Keywords: AD mouse model; AD therapy; Alzheimer’s disease; Cdc42; NSAIDs; Rac1; Rho GTPases; RhoA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological Modulators of Small GTPases of Rho Family in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 May 12;15:661612. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.661612. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34054432 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids extracted from leaves of Diospyros kaki regulates RhoA activity to rescue synapse loss and reverse memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice.Neuroreport. 2018 May 2;29(7):564-569. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000989. Neuroreport. 2018. PMID: 29481523
-
Approaches of targeting Rho GTPases in cancer drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015;10(9):991-1010. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2015.1058775. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 26087073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral effects of Rho GTPase modulation in a model of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Jan 15;237:223-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.09.043. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23026376
-
The potential role of rho GTPases in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Oct;50(2):406-22. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8637-5. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24452387 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Modulators of Small GTPases of Rho Family in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 May 12;15:661612. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.661612. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34054432 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the longitudinal stability of human plasma miRNAs and implications for disease biomarkers.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 25;14(1):2148. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52681-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38272952 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cdc42-intersectin interaction by small molecule ZCL367 impedes cancer cell cycle progression, proliferation, migration, and tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(6):740-749. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1564559. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30849276 Free PMC article.
-
CLN3, at the crossroads of endocytic trafficking.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Sep 25;762:136117. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136117. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 34274435 Free PMC article.
-
Clearing Amyloid-Beta by Astrocytes: The Role of Rho GTPases Signaling Pathways as Potential Therapeutic Targets.Brain Sci. 2024 Dec 10;14(12):1239. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121239. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

