Aptamer-Targeted Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy of Cancer
- PMID: 29246290
- PMCID: PMC5582647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.08.007
Aptamer-Targeted Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy of Cancer
Abstract
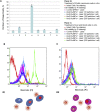
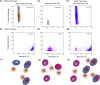
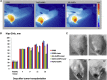
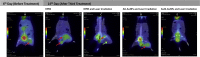
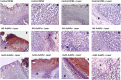
Novel nanoscale bioconjugates combining unique plasmonic photothermal properties of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with targeted delivery using cell-specific DNA aptamers have a tremendous potential for medical diagnostics and therapy of many cell-based diseases. In this study, we demonstrate the high anti-cancer activity of aptamer-conjugated, 37-nm spherical gold nanoparticles toward Ehrlich carcinoma in tumor-bearing mice after photothermal treatment. The synthetic anti-tumor aptamers bring the nanoparticles precisely to the desired cells and selectively eliminate cancer cells after the subsequent laser treatment. To prove tumor eradication, we used positron emission tomography (PET) utilizing radioactive glucose and computer tomography, followed by histological analysis of cancer tissue. Three injections of aptamer-conjugated AuNPs and 5 min of laser irradiations are enough to make the tumor undetectable by PET. Histological analysis proves PET results and shows lower damage of healthy tissue in addition to a higher treatment efficiency and selectivity of the gold nanoparticles functionalized with aptamers in comparison to control experiments using free unconjugated nanoparticles.
Keywords: DNA aptamer; computer tomography; gold nanoparticle; hyperthermia; mouse Ehrlich carcinoma; plasmonic photothermal therapy; positron emission tomography.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lapotko D.O., Lukianova E., Oraevsky A.A. Selective laser nano-thermolysis of human leukemia cells with microbubbles generated around clusters of gold nanoparticles. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006;38:631–642. - PubMed
-
- Zharov V.P., Galitovskaya E.N., Johnson C., Kelly T. Synergistic enhancement of selective nanophotothermolysis with gold nanoclusters: potential for cancer therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005;37:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Shi H., Ye X., He X., Wang K., Cui W., He D., II, Li D., Jia X. Au@Ag/Au nanoparticles assembled with activatable aptamer probes as smart “nano-doctors” for image-guided cancer thermotherapy. Nanoscale. 2014;6:8754–8761. - PubMed
-
- Kolovskaya O.S., Zamay T.N., Zamay A.S., Glazyrin Y.E., Spivak E.A., Zubkova O.A., Kadkina A.V., Erkaev E.N., Zamay G.S., Savitskaya A.G. DNA-aptamer/protein interaction as a cause of apoptosis and arrest of proliferation in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Biochemistry (Mosc). Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2014;8(1):60–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

