Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Intracellular Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting Hepadnaviral Replication
- PMID: 29246295
- PMCID: PMC5633256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.09.003
Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Intracellular Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting Hepadnaviral Replication
Abstract
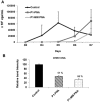
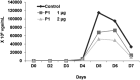
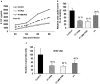
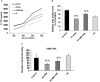
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) are potentially attractive antisense agents against hepatitis B virus (HBV), although poor cellular uptake limits their therapeutic application. In the duck HBV (DHBV) model, we evaluated different cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) for delivery to hepatocytes of a PNA-targeting hepadnaviral encapsidation signal (ε). This anti-ε PNA exhibited sequence-specific inhibition of DHBV RT in a cell-free system. Investigation of the best in vivo route of delivery of PNA conjugated to (D-Arg)8 (P1) showed that intraperitoneal injection to ducklings was ineffective, whereas intravenously (i.v.) injected fluorescein-P1-PNA reached the hepatocytes. Treatment of virus carriers with i.v.-administered P1-PNA resulted in a decrease in viral DNA compared to untreated controls. Surprisingly, a similar inhibition of viral replication was observed in vivo as well as in vitro in primary hepatocyte cultures for a control 2 nt mismatched PNA conjugated to P1. By contrast, the same PNA coupled to (D-Lys)4 (P2) inhibited DHBV replication in a sequence-specific manner. Interestingly, only P1, but not P2, displayed anti-DHBV activity in the absence of PNA cargo. Hence, we provide new evidence that CPP-PNA conjugates inhibit DHBV replication following low-dose administration. Importantly, our results demonstrate the key role of CPPs used as vehicles in antiviral specificity of CPP-PNA conjugates.
Keywords: CPP; DHBV; HBV; PNA; antiviral therapy; cell uptake; cell-penetrating peptide; duck hepatitis B virus; hepatitis B virus; peptide nucleic acid.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ott J.J., Stevens G.A., Groeger J., Wiersma S.T. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–2219. - PubMed
-
- Ocama P., Opio C.K., Lee W.M. Hepatitis B virus infection: current status. Am. J. Med. 2005;118:1413. - PubMed
-
- Mailliard M.E., Gollan J.L. Emerging therapeutics for chronic hepatitis B. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006;57:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Fischer K.P., Gutfreund K.S., Tyrrell D.L. Lamivudine resistance in hepatitis B: mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Resist. Updat. 2001;4:118–128. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen P.E. Antisense peptide nucleic acids. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2000;2:282–287. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

