Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Y-Box Binding Protein-1 Inhibit Tumor Angiogenesis by Downregulating Bcl-xL-VEGFR2/-Tie Axes
- PMID: 29246296
- PMCID: PMC5633255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.09.004
Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Y-Box Binding Protein-1 Inhibit Tumor Angiogenesis by Downregulating Bcl-xL-VEGFR2/-Tie Axes
Abstract
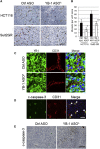
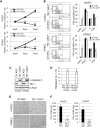
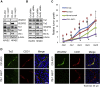
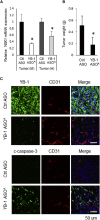
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1), involved in cancer progression and chemoradiation resistance, is overexpressed in not only cancer cells but also tumor blood vessels. In this study, we investigated the potential value of amido-bridged nucleic acid (AmNA)-modified antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeting YB-1 (YB-1 ASOA) as an antiangiogenic cancer therapy. YB-1 ASOA was superior to natural DNA-based ASO or locked nucleic acid (LNA)-modified YB-1 ASO in both knockdown efficiency and safety, the latter assessed by liver function. YB-1 ASOA administered i.v. significantly inhibited YB-1 expression in CD31-positive angiogenic endothelial cells, but not in cancer cells, in the tumors. With regard to the mechanism of its antiangiogenic effects, YB-1 ASOA downregulated both Bcl-xL/VEGFR2 and Bcl-xL/Tie signal axes, which are key regulators of angiogenesis, and induced apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. In the xenograft tumor model that had low sensitivity to anti-VEGF antibody, YB-1 ASOA significantly suppressed tumor growth; not only VEGFR2 but also Tie2 expression was decreased in tumor vessels. In conclusion, YB-1/Bcl-xL/VEGFR2 and YB-1/Bcl-xL/Tie signal axes play pivotal roles in tumor angiogenesis, and YB-1 ASOA may be feasible as an antiangiogenic therapy for solid tumors.
Keywords: ASO; Tie; VEGFR2; YB-1; tumor angiogenesis.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Crooke S.T. Antisense strategies. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004;4:465–487. - PubMed
-
- Wu H., Lima W.F., Zhang H., Fan A., Sun H., Crooke S.T. Determination of the role of the human RNase H1 in the pharmacology of DNA-like antisense drugs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:17181–17189. - PubMed
-
- Galarneau A., Min K.L., Mangos M.M., Damha M.J. Assay for evaluating ribonuclease H-mediated degradation of RNA-antisense oligonucleotide duplexes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005;288:65–80. - PubMed
-
- Vester B., Wengel J. LNA (locked nucleic acid): high-affinity targeting of complementary RNA and DNA. Biochemistry. 2004;43:13233–13241. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

