Exposure of the lungs in breast cancer radiotherapy: A systematic review of lung doses published 2010-2015
- PMID: 29246585
- PMCID: PMC5807032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.022
Exposure of the lungs in breast cancer radiotherapy: A systematic review of lung doses published 2010-2015
Abstract
Background and purpose: We report a systematic review of lung radiation doses from breast cancer radiotherapy.
Methods and materials: Studies describing breast cancer radiotherapy regimens published during 2010-2015 and reporting lung dose were included. Doses were compared between different countries, anatomical regions irradiated, techniques and use of breathing adaptation.
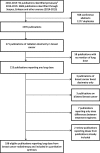
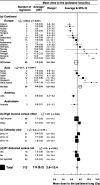
Results: 471 regimens from 32 countries were identified. The average mean ipsilateral lung dose (MLDipsi) was 9.0 Gy. MLDipsi for supine radiotherapy with no breathing adaption was 8.4 Gy for whole breast/chest wall (WB/CW) radiotherapy, 11.2 Gy when the axilla/supraclavicular fossa was irradiated, and 14.0 Gy with the addition of internal mammary chain irradiation; breathing adaptation reduced MLDipsi by 1 Gy, 2 Gy and 3 Gy respectively (p < 0.005). For WB/CW radiotherapy, MLDipsi was lowest for tangents in prone (1.2 Gy) or lateral decubitus (0.8 Gy) positions. The highest MLDipsi was for IMRT in supine position (9.4 Gy). The average mean contralateral lung dose (MLDcont) for WB/CW radiotherapy was higher for IMRT (3.0 Gy) than for tangents (0.8 Gy).
Conclusions: Lung doses from breast cancer radiotherapy varied substantially worldwide, even between studies describing similar regimens. Lymph node inclusion and IMRT use increased exposure, while breathing adaptation and prone/lateral decubitus positioning reduced it.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Breathing adaptation; Imrt; Lung dose.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exposure of the Heart in Breast Cancer Radiation Therapy: A Systematic Review of Heart Doses Published During 2003 to 2013.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015 Nov 15;93(4):845-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.2292. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015. PMID: 26530753
-
Prone versus supine free-breathing for right-sided whole breast radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 11;12(1):525. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04385-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35017568 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review for deep inspiration breath hold in proton therapy for mediastinal lymphoma: A PTCOG Lymphoma Subcommittee report and recommendations.Radiother Oncol. 2022 Dec;177:21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Radiother Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36252635
-
Positioning for acute respiratory distress in hospitalised infants and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 6;6(6):CD003645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003645.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35661343 Free PMC article.
-
Incidental axillary dose delivery to axillary lymph node levels I-III by different techniques of whole-breast irradiation: a systematic literature review.Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Sep;197(9):820-828. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01808-y. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 34292348
Cited by
-
Hypofractionated radiotherapy in postmastectomy locally advanced breast cancer: an interim report on acute toxicities and dosimetry.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022 Dec 29;27(6):943-953. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2022.0102. eCollection 2022. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022. PMID: 36632303 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of supine or prone crawl photon or proton breast and regional lymph node radiation therapy including the internal mammary chain.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 18;9(1):4755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41283-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30894606 Free PMC article.
-
Estimated Doses to the Heart, Lungs and Oesophagus and Risks From Typical UK Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer During 2015-2023.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024 Sep;36(9):e322-e332. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.05.002. Epub 2024 May 6. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024. PMID: 38853062 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Pneumonitis and Fibrosis in Cancer Therapy: A Review on Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(16):1505-1525. doi: 10.2174/1389450123666220907144131. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 36082868 Review.
-
DNA Strand Break Properties of Protoporphyrin IX by X-Ray Irradiation against Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 26;21(7):2302. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072302. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32225109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366:2087–2106. - PubMed
-
- Grantzau T., Overgaard J. Risk of second non-breast cancer after radiotherapy for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 762,468 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114:56–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

