Distinct subsets of Eve-positive pericardial cells stabilise cardiac outflow and contribute to Hox gene-triggered heart morphogenesis in Drosophila
- PMID: 29247145
- PMCID: PMC5825839
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.158717
Distinct subsets of Eve-positive pericardial cells stabilise cardiac outflow and contribute to Hox gene-triggered heart morphogenesis in Drosophila
Abstract
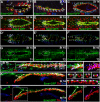
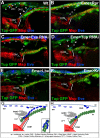
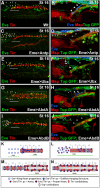
The Drosophila heart, composed of discrete subsets of cardioblasts and pericardial cells, undergoes Hox-triggered anterior-posterior morphogenesis, leading to a functional subdivision into heart proper and aorta, with its most anterior part forming a funnel-shaped cardiac outflow. Cardioblasts differentiate into Tin-positive 'working myocytes' and Svp-expressing ostial cells. However, developmental fates and functions of heart-associated pericardial cells remain elusive. Here, we show that the pericardial cells that express the transcription factor Even Skipped adopt distinct fates along the anterior-posterior axis. Among them, the most anterior Antp-Ubx-AbdA-negative cells form a novel cardiac outflow component we call the outflow hanging structure, whereas the Antp-expressing cells differentiate into wing heart precursors. Interestingly, Hox gene expression in the Even Skipped-positive cells not only underlies their antero-posterior diversification, but also influences heart morphogenesis in a non-cell-autonomous way. In brief, we identify a new cardiac outflow component derived from a subset of Even Skipped-expressing cells that stabilises the anterior heart tip, and demonstrate non-cell-autonomous effects of Hox gene expression in the Even Skipped-positive cells on heart morphogenesis.
Keywords: Drosophila; Heart; Hox genes; Pericardial cell.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drosophila cardiac tube organogenesis requires multiple phases of Hox activity.Dev Biol. 2004 Aug 15;272(2):419-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.04.036. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15282158
-
Heart tube patterning in Drosophila requires integration of axial and segmental information provided by the Bithorax Complex genes and hedgehog signaling.Development. 2002 Oct;129(19):4509-21. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.19.4509. Development. 2002. PMID: 12223408
-
Bithorax complex genes control alary muscle patterning along the cardiac tube of Drosophila.Mech Dev. 2009 May-Jun;126(5-6):478-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2009.01.001. Epub 2009 Jan 17. Mech Dev. 2009. PMID: 19272319 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular analysis of newly identified Hox downstream genes in Drosophila.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Feb-Mar;89(2-3):273-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.11.012. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20018403 Review.
-
Hox and Tale transcription factors in heart development and disease.Int J Dev Biol. 2018;62(11-12):837-846. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.180192sz. Int J Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30604853 Review.
Cited by
-
Hox Proteins in the Regulation of Muscle Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 18;9:731996. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.731996. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34733846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila as a Genetic Model for Hematopoiesis.Genetics. 2019 Feb;211(2):367-417. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300223. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30733377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell profiling of the developing embryonic heart in Drosophila.Development. 2023 Aug 15;150(16):dev201936. doi: 10.1242/dev.201936. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Development. 2023. PMID: 37526610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodmer R. and Frasch M. (2010). Development and aging of the Drosophila heart. In Heart Development and Regeneration (ed. Rosenthal N. and Harvey R. P.), pp. 47-86. Waltham, MA, USA: Academic Press.
-
- Brand A. H. and Perrimon N. (1993). Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118, 401-415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

