The Rising Incidence of Gout and the Increasing Burden of Comorbidities: A Population-based Study over 20 Years
- PMID: 29247151
- PMCID: PMC5880714
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.170806
The Rising Incidence of Gout and the Increasing Burden of Comorbidities: A Population-based Study over 20 Years
Abstract
Objective: To examine the incidence of gout over the last 20 years and to evaluate possible changes in associated comorbid conditions.
Methods: The medical records were reviewed of all adults with a diagnosis of incident gout in Olmsted County, Minnesota, USA, during 2 time periods (January 1, 1989-December 31, 1992, and January 1, 2009-December 31, 2010). Incident cases had to fulfill at least 1 of 3 criteria: the American Rheumatism Association 1977 preliminary criteria for gout, the Rome criteria, or the New York criteria.
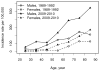
Results: A total of 158 patients with new-onset gout were identified during 1989-1992 and 271 patients during 2009-2010, yielding age- and sex-adjusted incidence rates of 66.6/100,000 (95% CI 55.9-77.4) in 1989-1992 and 136.7/100,000 (95% CI 120.4-153.1) in 2009-2010. The incidence rate ratio was 2.62 (95% CI 1.80-3.83). At the time of their first gout flare, patients diagnosed with gout in 2009-2010 had higher prevalence of comorbid conditions compared with 1989-1992, including hypertension (69% vs 54%), diabetes mellitus (25% vs 6%), renal disease (28% vs 11%), hyperlipidemia (61% vs 21%), and morbid obesity (body mass index ≥ 35 kg/m2; 29% vs 10%).
Conclusion: The incidence of gout has more than doubled over the recent 20 years. This increase together with the more frequent occurrence of comorbid conditions and cardiovascular risk factors represents a significant public health challenge.
Keywords: COMORBIDITY; EPIDEMIOLOGY; GOUT; INCIDENCE.
Figures
Comment in
-
A Changing Landscape of Gout: Comorbidity Matters.J Rheumatol. 2018 Apr;45(4):454-455. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.171446. J Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29606645 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3136–41. - PubMed
-
- Portis AJ, Laliberte M, Tatman P, Moua M, Culhane-Pera K, Maalouf NM, et al. High prevalence of gouty arthritis among the Hmong population in Minnesota. Arthritis Care Res. 2010;62:1386–91. - PubMed
-
- Arromdee E, Michet CJ, Crowson CS, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Epidemiology of gout: is the incidence rising? J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2403–6. - PubMed
-
- Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, Wortmann R. Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1582–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical