Real-time decoding of covert attention in higher-order visual areas
- PMID: 29247807
- PMCID: PMC5864512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.019
Real-time decoding of covert attention in higher-order visual areas
Abstract
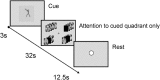
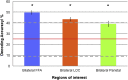
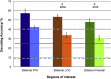
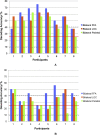
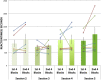
Brain-computer-interfaces (BCI) provide a means of using human brain activations to control devices for communication. Until now this has only been demonstrated in primary motor and sensory brain regions, using surgical implants or non-invasive neuroimaging techniques. Here, we provide proof-of-principle for the use of higher-order brain regions involved in complex cognitive processes such as attention. Using realtime fMRI, we implemented an online 'winner-takes-all approach' with quadrant-specific parameter estimates, to achieve single-block classification of brain activations. These were linked to the covert allocation of attention to real-world images presented at 4-quadrant locations. Accuracies in three target regions were significantly above chance, with individual decoding accuracies reaching upto 70%. By utilising higher order mental processes, 'cognitive BCIs' access varied and therefore more versatile information, potentially providing a platform for communication in patients who are unable to speak or move due to brain injury.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Allison, B.Z., Wolpaw, E.W., Wolpaw, J.R., Wolpaw, W., 2007. Brain – computer interface systems : progress and prospects 463–474. - PubMed
-
- Andersson P., Viergever M.A., Pluim J.P.W., Ramsey N.F., Siero J.C.W. 2009 4th Int. IEEE/EMBS Conf. Neural Eng. 2009. fMRI based BCI control using spatial visual attention at 7T; pp. 444–446.
-
- Andersson P., Ramsey N.F., Pluim J.P.W., Viergever M.A. BCI control using 4 direction spatial visual attention and real-time fMRI at 7T. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2010;2010:4221–4225. - PubMed
-
- Andersson P., Ramsey N.F., Raemaekers M., Viergever M.A., Pluim J.P.W. Real-time decoding of the direction of covert visuospatial attention. J. Neural. Eng. 2012;9:45004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

