Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 29247988
- PMCID: PMC7165732
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12616
Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis
Abstract
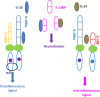
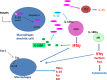
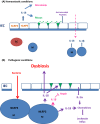
Initially described as an interferon (IFN)γ-inducing factor, interleukin (IL)-18 is indeed involved in Th1 and NK cell activation, but also in Th2, IL-17-producing γδ T cells and macrophage activation. IL-18, a member of the IL-1 family, is similar to IL-1β for being processed by caspase 1 to an 18 kDa-biologically active mature form. IL-18 binds to its specific receptor (IL-18Rα, also known as IL-1R7) forming a low affinity ligand chain. This is followed by recruitment of the IL-18Rβ chain. IL-18 then uses the same signaling pathway as IL-1 to activate NF-kB and induce inflammatory mediators such as adhesion molecules, chemokines and Fas ligand. IL-18 also binds to the circulating high affinity IL-18 binding protein (BP), such as only unbound free IL-18 is active. IL-18Rα may also bind IL-37, another member of the IL-1 family, but in association with the negative signaling chain termed IL-1R8, which transduces an anti-inflammatory signal. IL-18BP also binds IL-37 and this acts as a sink for the anti-inflammatory properties of IL-37. There is now ample evidence for a role of IL-18 in various infectious, metabolic or inflammatory diseases such as influenza virus infection, atheroma, myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or Crohn's disease. However, IL-18 plays a very specific role in the pathogenesis of hemophagocytic syndromes (HS) also termed Macrophage Activation Syndrome. In children affected by NLRC4 gain-of-function mutations, IL-18 circulates in the range of tens of nanograms/mL. HS is treated with the IL-1 Receptor antagonist (anakinra) but also specifically with IL-18BP. Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis or adult-onset Still's disease are also characterized by high serum IL-18 concentrations and are treated by IL-18BP.
Keywords: hemophagocytic syndromes; inflammatory diseases; interferon γ; interleukin-1; interleukin-18; interleukin-18 binding protein.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Okamura H, Tsutsi H, Komatsu T, et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN‐gamma production by T cells. Nature. 1995;378:88‐91. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. IL‐18: A TH1‐inducing, proinflammatory cytokine and new member of the IL‐1 family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:11‐24. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin‐18. Methods. 1999;19:121‐132. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi K, Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Okamura H. Interleukin‐18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:423‐474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

