GDC-0879, a BRAFV600E Inhibitor, Protects Kidney Podocytes from Death
- PMID: 29249695
- PMCID: PMC5819995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.11.006
GDC-0879, a BRAFV600E Inhibitor, Protects Kidney Podocytes from Death
Abstract
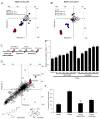
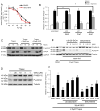
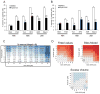
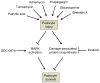
Progressive kidney diseases affect approximately 500 million people worldwide. Podocytes are terminally differentiated cells of the kidney filter, the loss of which leads to disease progression and kidney failure. To date, there are no therapies to promote podocyte survival. Drug repurposing may therefore help accelerate the development of cures in an area of tremendous unmet need. In a newly developed high-throughput screening assay of podocyte viability, we identified the BRAFV600E inhibitor GDC-0879 and the adenylate cyclase agonist forskolin as podocyte-survival-promoting compounds. GDC-0879 protects podocytes from injury through paradoxical activation of the MEK/ERK pathway. Forskolin promotes podocyte survival by attenuating protein biosynthesis. Importantly, GDC-0879 and forskolin are shown to promote podocyte survival against an array of cellular stressors. This work reveals new therapeutic targets for much needed podocyte-protective therapies and provides insights into the use of GDC-0879-like molecules for the treatment of progressive kidney diseases.
Keywords: BRAF; ER stress; ERK; MAPK; SB-682330; cell death; forskolin; glomerular disease; kidney disease; melanoma; post-mitotic cells.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests.
P.M. declares equity in Goldfinch Biopharma. A.G. has a financial interest in Goldfinch Biopharma, which was reviewed and is managed by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Partners HealthCare and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. A.G. also declares consultation services for Bristol Myers Squibb and Third Rock Ventures.
Figures

Comment in
-
Screening Drugs for Kidney Disease: Targeting the Podocyte.Cell Chem Biol. 2018 Feb 15;25(2):126-127. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.01.018. Cell Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29452609
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

