Mapping the Growing Discipline of Dissemination and Implementation Science in Health
- PMID: 29249842
- PMCID: PMC5729761
- DOI: 10.1007/s11192-017-2455-2
Mapping the Growing Discipline of Dissemination and Implementation Science in Health
Abstract
Background: The field of dissemination and implementation (D&I) research in health has grown considerably in the past decade. Despite the potential for advancing the science, limited research has focused on mapping the field.
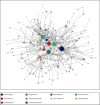
Methods: We administered an online survey to individuals in the D&I field to assess participants' demographics and expertise, as well as engagement with journals and conferences, publications, and grants. A combined roster-nomination method was used to collect data on participants' advice networks and collaboration networks; participants' motivations for choosing collaborators was also assessed. Frequency and descriptive statistics were used to characterize the overall sample; network metrics were used to characterize both networks. Among a sub-sample of respondents who were researchers, regression analyses identified predictors of two metrics of academic performance (i.e., publications and funded grants).
Results: A total of 421 individuals completed the survey, representing a 30.75% response rate of eligible individuals. Most participants were White (n = 343), female (n = 284, 67.4%), and identified as a researcher (n = 340, 81%). Both the advice and the collaboration networks displayed characteristics of a small world network. The most important motivations for selecting collaborators were aligned with advancing the science (i.e., prior collaborators, strong reputation, and good collaborators) rather than relying on human proclivities for homophily, proximity, and friendship. Among a sub-sample of 295 researchers, expertise (individual predictor), status (advice network), and connectedness (collaboration network) were significant predictors of both metrics of academic performance.
Conclusions: Network-based interventions can enhance collaboration and productivity; future research is needed to leverage these data to advance the field.
Keywords: Network science; dissemination science; implementation science; network analysis; scientometrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests NSC is the co-founder and Chairman of Syndio. WEN, AL and DAC have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Global Implementation Conference. [ http://gic.globalimplementation.org/]
-
- KT Canada Summer Institute on Knowledge Translation. [ http://ktclearinghouse.ca/ktcanada/education/summerinstitute]
-
- Brownson RC. Mentored Training for Dissemination and Implementation Research in Cancer. National Cancer Institute; 2013.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
